Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
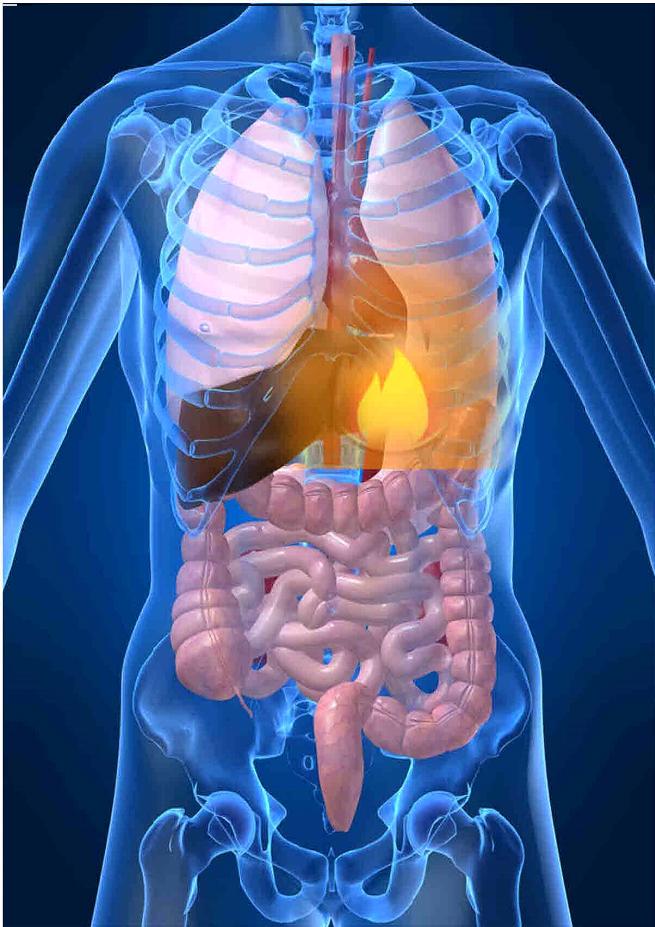
What Is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease?
It is a digestive disease that occurs when the stomach acid rolls back into the esophagus. Such tend to cause inflammation of the esophagus lining, leading the chronic disease, GERD.
One may experience the two digestive conditions, heartburn and acid reflux from time to time. In case these symptoms disturb your everyday life, occur more than once every week, or the doctor have spotted any damage to the esophagus, then chances of being detected with gastroesophageal reflux disease is high.
Discomfort associated with the disease can be eased with over-the-counter drugs and making certain changes in the lifestyle. Though, to decrease the severity of symptoms, few patients are advice the option of surgery or stronger medications.
What Are The Symptoms Of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease?
Symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease are:
- Chest pain.
- Swallowing difficulties, commonly known as dysphagia.
- Heartburn, the burning sensation may spread to the throat, accompanied with a sour taste.
- Dry cough.
- Sore throat or hoarseness.
- Feeling of a lump while swallowing food.
- Acid reflux, regurgitation of sour liquid or food.
What Causes Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease?
Recurrent acid reflux is responsible for causing gastroesophageal reflux disease. Acid reflux is the rolling back of bile or stomach acid into your esophagus. When we swallow food, our lower esophageal sphincter tends to relaxes, to let the liquid or solid move down into the stomach. After this, the lower esophageal sphincter closes again.
Though, in case it become weak or fails to relax normally, acid in our stomach rolls back, reaching the esophagus. This leads to heartburn. Frequent occurrence of acid reflux may irritate and inflame the esophagus lining. Such can cause damage to it, resulting in complications, for example bleeding, Barrett’s esophagus etc.
What Are The Risk Factors Of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease?
Factors identified for raising the risk of developing gastroesophageal reflux disease are:
- Diabetes.
- Asthma.
- Dry mouth.
- Smoking.
- Pregnancy.
- Hiatal hernia.
- Obesity.
- Connective tissue disorders.
- Delayed stomach emptying.
What Are The Complications Of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease?
Gradually, chronic inflammation in the esophagus can lead to a number of complications, few of which are:
- Barrett’s esophagus.
- Esophageal ulcer.
- Esophageal.
How Is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Diagnosed?
The following may help diagnose gastroesophageal reflux disease:
- Symptoms of the patient.
- Test to examine the level of acid in the esophagus.
In case the doctor suggests surgery as the treatment option for your case, then you may undergo the following tests as well:
- X-ray (upper digestive system).
- Test for measuring your esophagus movement.
- Placing a tube to see inside the esophagus.
How Is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment?
Usually, patient starts with over-the-counter drugs to ease the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease. However, if the symptoms fail to respond the medications, then your doctor will review other treatment options including surgery and medications.
By : Natural Health News