Vaginal Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
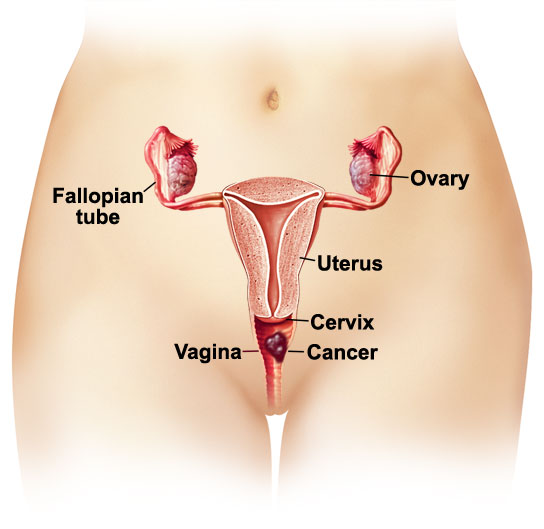
What Is Vaginal Cancer?
Vaginal cancer is a form of cancer which forms in the tissues of the vagina. It involves the formation of malignant cells in the vagina. Although it can occur in any age, it mostly affects women over the age of 50.
Treatment involves surgery along with pelvic radiation.
Vaginal cancer is relatively rare. When found in early stages, it can often be cured. There are two main types of vaginal cancer:
- Squamous cell carcinoma:
Squamous cell vaginal cancer spreads gradually and is confined near the vagina, but may spread to the lungs and liver.
The most common type of vaginal cancer, it is mostly found in women aged 60 or older. - Adenocarcinoma:
Adenocarcinoma begins in glandular cells.
Adenocarcinoma has a higher probability than squamous cell cancer to spread to the lungs and lymph nodes.
It is found most often in women aged 30 or younger.
Causes Of Vaginal Cancer:
The exact cause of vaginal cancer is yet unknown.
However, the process is similar to other type of cancers. It begins with genetic mutations of cells of the tissues lining the vagina, due to error in their DNA. This causes the cells to divide uncontrollably, which leads to the formation of a tumor.
Certain factors increase the risk of developing vaginal cancer. They include:
- Being infected with the human papilloma virus (HPV), a virus that can be transmitted sexually.
- Age- the older the individual is, the higher the chances of developing the disease
- A previous history of vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia (VAIN) or cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), which are abnormal cells in the vagina or cervix that can sometimes become cancerous
- Having had hysterectomy performed
Symptoms Of Vaginal Cancer:
Generally, women who suffer from vaginal cancer may not exhibit any symptoms initially.
As the cancer spreads, the following symptoms may be exhibited:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Difficulty or pain when urinating
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Pain in the pelvic area (the lower part of the abdomen between the hip bones)
- Pain in the back or legs
- Swelling in the legs
- A lump or mass in the vagina
- Constipation
- Unusual bleeding- after menopause or sexual intercourse
Diagnosis Of Vaginal Cancer:
The following tests can help diagnose vaginal cancer:
- Physical exam and history
- Pelvic exam
- Pap smear
- Biopsy
- Colposcopy
Treatment Of Vaginal Cancer:
The following treatment options are available:
- Surgery
Laser surgery
Excision
Vaginectomy
Radical hysterectomy - Radiation therapy
External beam radiation therapy - Chemotherapy
Related Articles:
Esophageal Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Thyroid Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Rectal Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Testicular Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Vulvar Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Gallbladder Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Pancreatic Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Case Seeking Cancer Screenings Heads To Trial
Solid Organ Transplant Patients At Higher Cancer Death Risk
A Sort Of Prostate Cancer Treatment May Upsurge Probabilities Of Alzheimer’s
Oral Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Ovarian Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Alkaline Diet Helping In Cancer and Other Syndromes
By : Natural Health News




