Stress Fractures Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
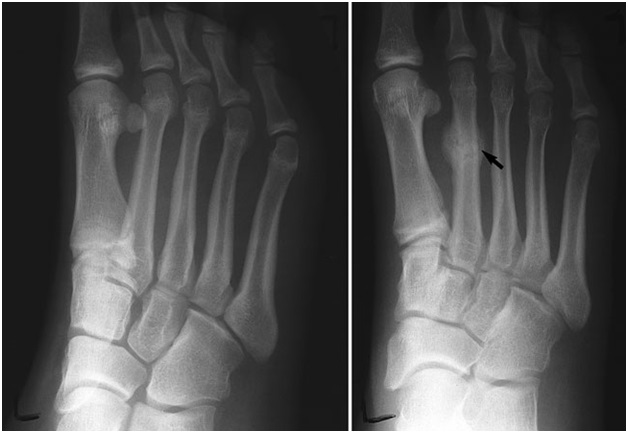
What Is Stress Fracture ?
Also known as hairline fracture, a stress fracture is a fatigue induced fracture where the muscles become tired and are unable to absorb the added stress placed upon them over time.
Eventually, such a muscle transfers its load on to the bone which causes a fracture called stress fracture. Moreover, stress fracture may also arise from weakened bones, which may happen due to development of osteoporosis.
Rather than being a product of a single severe impact, stress fractures are an outcome of accumulated trauma from repeated sub maximal loading. This may include running and jumping.
This characteristic means that stress fracture is highly common in athletes. Often described as a very small crack in the bone, stress fractures usually affect weight bearing bones, such as tibia, metatarsals and navicular bones.
Causes Of Stress Fractures:
Stress factors are caused by increasing the intensity of an activity, such as running and jumping, for an extended period. This causes the muscles to become fatigued and transfer their load to bones.
If the load placed on the bone exceeds its natural remodeling capacity, a stress fracture may appear. Such an event does not occur suddenly, but results from repeated traumas.
Other factors which may increase the risk of developing stress fractures include:
- A sedentary person suddenly undertaking a burst of exercise
- Having developed a stress fracture in the past
- Conditions which cause bone insufficiency
- Osteoporosis
- Use of certain long term medications
- Poor conditioning
- Improper technique
- Altering the mechanics of how foot naturally absorbs impact
- Happens if the affected individual has bunions, blisters or tendonitis
- Change in training or playing surface
- Improper equipment
- Wearing flimsy shoes
Symptoms Of Stress Fractures:
The only symptom exhibited by stress fractures is the presence of pain and swelling in the affected bone.
The pain usually begins while an act of weight bearing and usually subsides with rest. However, if the stress fracture is severe, the pain may persist even when resting.
The affected bone is also marked by localized tenderness and a generalized swelling in that area.
Diagnosis Of Stress Fractures:
Stress fractures can be diagnosed via:
- A medical history
- Physical exam
- Imaging tests, to detect the presence of stress fractures
- X-rays
- Bone scan
- MRI
Treatment Of Stress Fracture:
The initial treatment for stress fracture focuses on resting while the bone heals itself. This is accompanied by reducing activities and icing the affected area.
In order to relieve pain, pain killers may be prescribed. Common painkillers include ibuprofen and paracetemol.
Moreover, a cast or walking boot is used for a period of four to eight weeks. If the Stress fracture is serious, surgery may be recommended.
By : Natural Health News




