Epidermoid Cysts Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
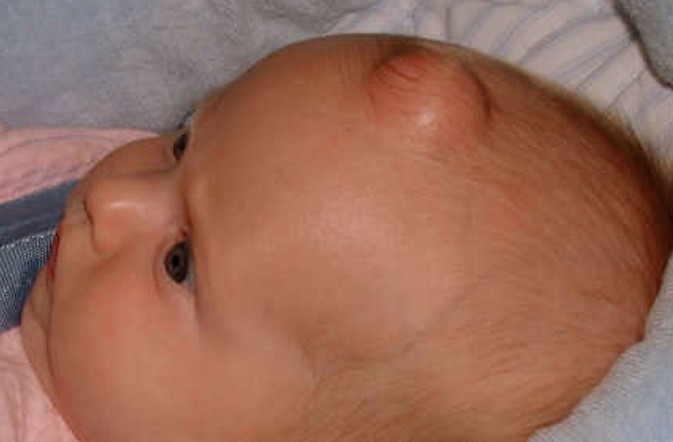
What are Epidermoid Cysts?
An epidermoid cyst is a benign cyst usually found on the skin. The cyst develops out of ectodermal tissue.
Epidermoid cysts can appear anywhere on the skin, but are most common on the face, neck and trunk.
Historically, epidermoid cysts have been referred to by various terms, including follicular infundibular cysts, epidermal cysts, and epidermal inclusion cysts.
Causes of Epidermoid Cysts:
The surface of the skin (epidermis) is made up of a thin, protective layer of cells that the body continuously sheds. Most epidermoid cysts form when these cells move deeper into the skin and multiply rather than slough off.
The epidermal cells form the walls of the cyst and then secrete the protein keratin into the interior. The keratin is the thick, yellow substance that sometimes drains from the cyst. This abnormal growth of cells may be due to a damaged hair follicle or oil gland in the skin.
Many people refer to epidermoid cysts as sebaceous cysts, but they’re different. True sebaceous cysts are less common. They arise from the glands that secrete oily matter that lubricates hair and skin (sebaceous glands).
The following factors increase the probability of developing epidermoid cyst:
- Being past puberty
- Having a history of acne
- Having certain rare genetic disorders
- Injuring the skin
Symptoms of Epidermoid Cysts:
The following symptoms are exhibited:
- A small, round bump under the skin, usually on the face, trunk or neck
- A tiny blackhead plugging the central opening of the cyst
- A thick, yellow, foul-smelling material that sometimes drains from the cyst
- Redness, swelling and tenderness in the area, if inflamed or infected
Diagnosis of Epidermoid Cysts:
Epidermoid cysts are diagnosed via the following;
- Physical examination
- Biopsy
Treatment of Epidermoid Cyst:
The following treatment options are available:
- Injection.
- This treatment involves injecting the cyst with a medicine that reduces swelling and inflammation.
- Incision and drainage.
- With this method, the doctor makes a small cut in the cyst and gently squeezes out the contents.
- Minor surgery.
- The doctor can remove the entire cyst.
- Minor surgery is safe and effective and usually prevents cysts from recurring.
- Lasers.
- This method involves using a carbon dioxide laser to vaporize the cyst. It results in minimal scarring.
By : Natural Health News




