HPV Infection Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What is HPV Infection?
Human papilloma virus (HPV) is a viral infection that is passed between people through skin-to-skin contact.
There are more than 100 varieties of HPV, but most emphasis is given to the 40 varieties that affect the genitals, mouth, or throat, that are passed through sexual contact.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection that affects both men and women.
Causes of HPV Infection:
Most people get HPV through direct sexual contact or oral sex.
Since HPV is a skin-to-skin infection, intercourse isn’t required to contract the infection.
In rare cases, an infected mother can infect her baby during delivery.
All in all, HPV virus can be transmitted via:
- Perinatal transmission
- Genital infections
- Hands
- Shared objects
- Blood
- Surgery
The following factors increase the risk of acquiring HPV infection:
- Number of sexual partners.
- The greater the number of sexual partners, the higher the chances of contracting HPV infection
- Having sex with a partner who has multiple sex partners increases the risk of developing HPV infection
- Common warts occur most often in children.
- While plantar warts may occur in adults, they’re more likely to initially surface on adolescents or young adults.
- Genital warts occur most often in adolescents and young adults.
- Weakened immune systems.
- People who have weakened immune systems are at greater risk of HPV infections.
- Damaged skin.
- Areas of skin that have been punctured or opened are more prone to develop common warts.
- Personal contact.
- Touching someone’s warts or not wearing protection before contacting surfaces that have been exposed to HPV may increase risk of HPV infection.
Symptoms of HPV Infection:
Generally, the body’s immune system defeats a HPV infection before it can exhibit symptoms.
However, if symptoms do appear, they are characterized by warts which may vary in appearance depending on which variety of HPV is involved.
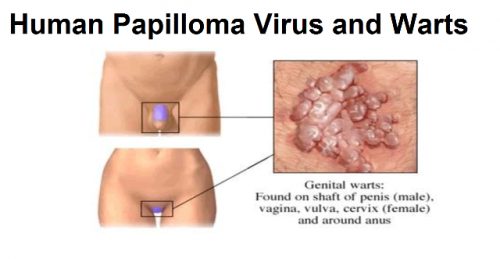
- Genital warts
- Common warts
- Plantar warts
- Flat warts
Moreover, HPV infection is one of the most important infectious causes of cancer.
- cervical cancer
- anal cancer
- vulvar cancer
- vaginal cancer
- penile cancer
- Head and neck cancer
Diagnosis of HPV Infection:
HPV infection can be diagnosed via:
- Visual inspection of warts and lesions
- Vinegar (acetic acid) solution test, to identify flat lesions
- Pap test, to reveal abnormalities that may lead to cancer
- DNA test, to recognize the DNA of the high-risk varieties of HPV that have been linked to genital cancers
Treatment of HPV Infection:
The following treatment options are available;
- Medications
- Salicylic acid.
- Imiquimod
- Aldara
- Zyclara
- Podofilox (Condylox).
- Trichloroacetic acid.
- Surgical procedures
Physically removing warts by:
- Freezing with liquid nitrogen (cryotherapy)
- Burning with an electrical current (electrocautery)
- Surgical removal
- Laser surgery
By : Natural Health News




