Cellulitis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What is Cellulitis?
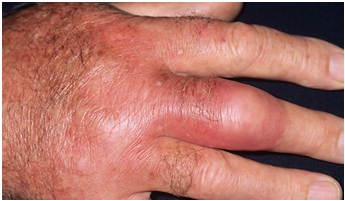
Cellulitis is a common, potentially serious bacterial skin infection. Cellulitis appears as a swollen, red area of skin that feels hot and tender. It can spread rapidly to other parts of the body. Skin on lower legs is most commonly affected, though cellulitis can occur anywhere on your body or face. Cellulitis might affect only your skin’s surface. Or it might also affect tissues underlying your skin and can spread to your lymph nodes and bloodstream.
Causes of Cellulitis
Staphylococcus and streptococcus bacteria are the most common causes of cellulitis. Risk factors for cellulitis include:
- Cracks or peeling skin between the toes
- History of peripheral vascular disease
- Injury or trauma with a break in the skin (skin wounds)
- Insect bites and stings, animal bites, or human bites
- Ulcers from certain diseases, including diabetes and vascular disease
- Use of corticosteroid medications or medications that suppress the immune system
- Wound from a recent surgery
Symptoms of Cellulitis
Symptoms of Cellulitis develop abruptly and can get worse rapidly. It affects the skin and can also cause additional symptoms. Cellulitis causes the affected skin to become:
- red
- hot
- swollen
- painful
- tender
There may also be a break in the skin, although this isn’t always obvious, and pus or blood-filled blisters.
Cellulitis can also cause additional symptoms that may develop before or alongside the changes to your skin.
These can include:
- feeling generally unwell
- feeling sick
- shivering
- chills
Occasionally the infection can extend to other parts of the body, such as the deeper layers of tissue, blood, muscle and bone. This can be very severe and potentially life threatening.
Signs the infection has spread include:
- a high temperature (fever) of 38C (100.4F) or above
- a fast heartbeat or fast breathing
- being sick
- diarrhea
- feeling dizzy or faint
- confusion or disorientation
- cold, clammy, pale skin
- unresponsiveness or loss of consciousness
Diagnosis of Cellulitis
The health care provider will perform a physical exam. This may reveal:
- Redness, warmth, and swelling of the skin
- Possible drainage, if there is a buildup of pus (abscess) with the skin infection
- Swollen glands (lymph nodes) near the affected area
Tests that may be ordered include:
- Blood culture
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Culture of any fluid or material inside the affected area
- A biopsy may be done if other conditions are suspected
Treatment of Cellulitis
- Antibiotics
- Raise the infected area higher than your heart to reduce swelling.
- Rest
You may need to stay in a hospital if:
- You are very sick (for example, you have a very high temperature, blood pressure problems, or nausea and vomiting that does not go away)
- You have been on antibiotics and the infection is getting worse (spreading beyond the original pen marking)
- Your immune system is not working well (due to cancer, HIV)
- You have an infection around your eyes
- You require antibiotics through a vein (IV)
Related Articles:
Swimmers Itch Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Tularemia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and treatment
Cold Sores Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Hemangioma Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Progeria Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Raynaud’s Disease Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Stye Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Castleman Disease Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Diaper Rash Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Tinea Versicolor Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Prickly Heat Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
By : Natural Health News




