Sebaceous Cyst Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
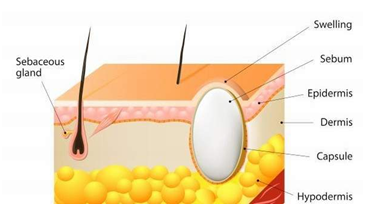
What is Sebaceous Cyst?
Sebaceous cysts are common noncancerous growth of the skin. Cysts are anomalies in the body that may contain liquid or semi liquid material. These cysts are closed sacs that can be found under the skin of the whole body, except for the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. A cyst usually is a slow-growing lump that can move easily under the skin. A foul odor may be seen from the overlying skin. Basically the term alludes to either an “epidermis cyst,” which originates from the skin, or a “pillar cyst,” which comes from hair follicles.
Causes of Sebaceous Cyst
Sebaceous cysts form out of your sebaceous gland. The sebaceous gland produces the oil called sebum that coats your hair and skin. Cysts can develop if the gland or its duct, the passage where oil is able to leave, becomes damaged or blocked. This usually occurs due to a trauma to the area. The trauma may be a scratch, a surgical wound, or a skin condition, such as acne. Sebaceous cysts grow slowly, so the trauma may have occurred months or weeks before the cyst visible. Therefore, blocked glands or swollen hair follicles in the skin may be the cause.
Trauma to skin has been the cause, as well. Cysts sometimes are hereditary.
Other causes of a sebaceous cyst may include:
- A misshapen or deformed duct
- Damage to the cells during a surgery
- Genetic conditions, such as Gardner’s syndrome or basal cell nevus syndrome
Symptoms of Sebaceous Cyst
The primary symptom of a sebaceous cyst is a small lump under the skin. The lump usually is not painful. In some cases, however, cysts can get inflamed and become painful to the touch. There may be redness and increased temperature of the skin on the area of the cyst. Drainage from the cyst will appear grayish-white and cheese-like and have a foul odor.
A sebaceous cyst is considered abnormal and possibly cancerous, if it has the following characteristics:
- A diameter that is larger than five centimeters
- A fast rate of reoccurrence after being removed
- Signs of infection, such as redness, pain, or pus drainage
Diagnosis of Sebaceous Cyst
Cyst can be diagnosed with a simple examination of the skin. Common tests used for a sebaceous cyst include:
- CT scans.
- Ultrasound.
- Biopsy.
Treatment of Sebaceous Cyst
Cyst can be leave alone if it doesn’t cause discomfort or cosmetic problems. Following are the treatment options available:
- Injection. This treatment involves injecting the cyst with a medicine that reduces swelling and inflammation.
- Incision and drainage. With this method, a small cut is made in the cyst and gently squeezes out the contents. This is a fairly quick and easy method, but cysts often recur after this treatment.
- Minor surgery. Minor surgery is safe and effective and usually prevents cysts from recurring, as entire cyst is removed.
- Lasers. This method involves using a carbon dioxide laser to vaporize the cyst. It results in minimal scarring.
By : Natural Health News




