Ovarian Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
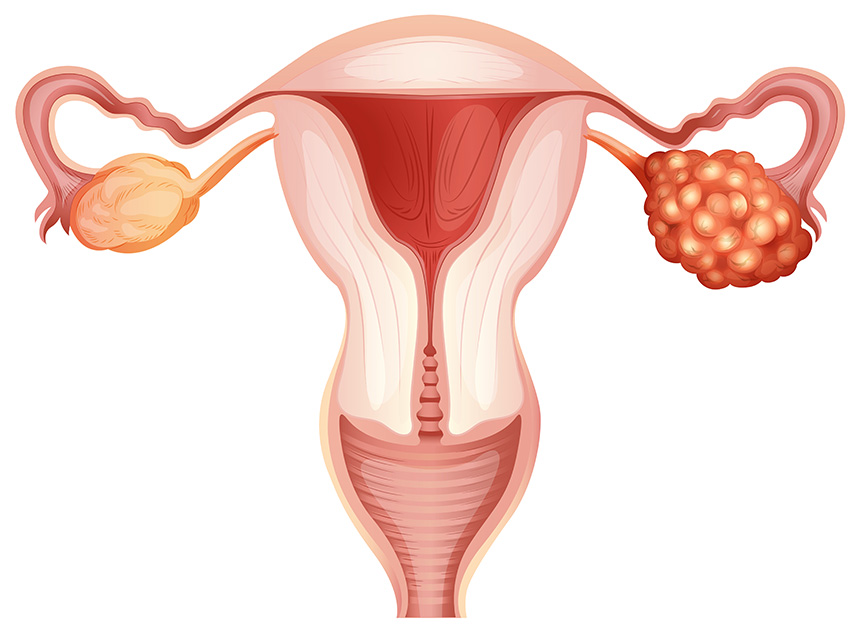
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the ovaries. It results in abnormal cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body.
Ovarian cancer often goes undetected until it has spread within the pelvis and abdomen. In such a late stage, ovarian cancer is more difficult to treat and is frequently fatal.
Early-stage ovarian cancer, in which the disease is confined to the ovary, is more likely to be treated successfully.
Ovarian cancer can be subdivided into the following types:
- Epithelial tumors, which begin in the thin layer of tissue that covers the outside of the ovaries.
- Stromal tumors, which begin in the ovarian tissue that contains hormone-producing cells.
- Germ cell tumors, which begin in the egg-producing cells.
Causes of Ovarian Cancer:
The underlying cause of ovarian cancer is yet unknown,
However, certain factors are known to increase the risk of developing ovarian cancer. These may include:
- Being 50 to 60 years of age
- Inherited gene mutation
- Being a recipient of estrogen replacement therapy
- Age when menstruation started and ended ( if menstruation starts before the age of 12 and menopause starts after 52, one is at a higher risk of developing ovarian cancer)
- Never being pregnant
- Being a recipient of fertility treatment
- Smoking
- Using intrauterine device
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer:
Early stage of ovarian cancer doe not exhibit any sign or symptoms and therefore is difficult to detect.
The following symptoms are seen in later stages of ovarian cancer:
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
- Quickly feeling full when eating
- Weight loss
- Discomfort in the pelvis area
- Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation
- A frequent need to urinate
- Abdominal or pelvic pain
- Back pain
- Irregular menstruation or postmenopausal vaginal bleeding,
- Pain or bleeding after or during sexual intercourse,
- Difficulty eating
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Diarrhea
- Indigestion
- Heartburn
- Constipation
- Nausea
- Early satiety
Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer:
The following tests and exams confirm the diagnosis of ovarian cancer:
- Pelvic exam
This includes the following steps:
- The outer part of genitals is carefully inspected.
- The doctor then inserts two gloved fingers into the vagina and simultaneously presses a hand on the abdomen to feel the uterus and ovaries.
- A device (speculum) is inserted into the vagina so that the doctor can visually check for abnormalities.
- Imaging tests
- Ultrasound
- CT scan
- Blood test
- Surgery to remove a tissue sample
Treatment of Ovarian Cancer:
Treatment targeted against ovarian cancer is a combination of chemotherapy and surgery.
- Surgery
Treatment generally involves removing both of the ovaries, the fallopian tubes, and the uterus as well as nearby lymph nodes and a fold of fatty abdominal tissue (omentum) where ovarian cancer often spreads.
- Chemotherapy
After surgery, chemotherapy is used to kill any remaining cancer cells.
Related Articles:
Esophageal Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Thyroid Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Vaginal Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Rectal Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Testicular Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Vulvar Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Gallbladder Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Pancreatic Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Case Seeking Cancer Screenings Heads To Trial
Solid Organ Transplant Patients At Higher Cancer Death Risk
A Sort Of Prostate Cancer Treatment May Upsurge Probabilities Of Alzheimer’s
Oral Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Alkaline Diet Helping In Cancer and Other Syndromes
By : Natural Health News




