Oral Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
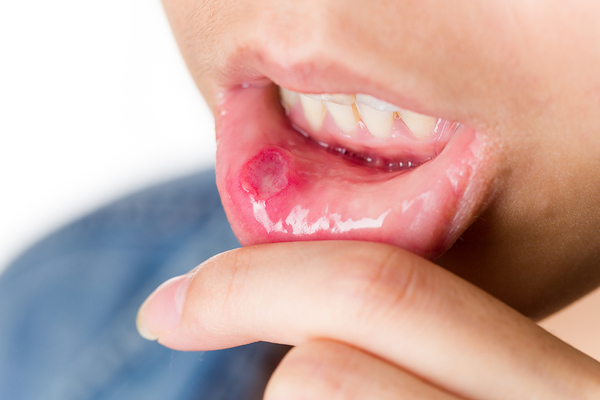
What is Oral Cancer?
Oral Cancer can form in any part of the mouth. Most oral cancers begin in the flat cells that cover the surfaces of your mouth, tongue, and lips. Anyone can get oral cancer, but the risk is higher if you are male, use tobacco, drink lots of alcohol, have HPV Infection, or have a history of head or neck cancer.
Causes of Oral Cancer
A cancerous (malignant) tumour starts from one abnormal cell. The exact reason why a cell becomes cancerous is unclear. It is thought that something damages or alters certain genes in the cell. This makes the cell abnormal and multiply out of control. Some people develop mouth cancer for no apparent reason. However, certain risk factors increase the chance that mouth cancer may develop. These include:
- Smoking: Oral cancer is just one cancer which has a much higher incidence in smokers than in non-smokers.
- Alcohol: Drinking a lot of alcohol can increase your risk of developing mouth cancer.
- Chewing tobacco or the betal leaf.
- Poor dental hygiene.
- Dietary factors (eating a well-balanced diet – high in fruits, vegetables and fish and low in high-fat and cholesterol meats, rice and refined grains – can reduce the risk of oral cancer).
- The human papillomavirus (HPV) may increase your risk of mouth cancer.
- There are some conditions affecting the mouth, such as leukoplakia and erythroplakia, which can increase the risk of a cancer developing.
Symptoms of Oral Cancer
The most common symptoms of oral cancer are:
- Sore mouth ulcers that don’t heal within several weeks
- Unexplained, persistent lumps in the mouth that don’t go away
- Unexplained, persistent lumps in the lymph glands in the neck that don’t go away
Other symptoms may include:
- Pain or difficulty when swallowing (dysphagia)
- Changes in your voice or speech problems
- Unexplained weight loss
- Bleeding or numbness in the mouth
- A tooth, or teeth, that becomes loose for no obvious reason, or a tooth socket that doesn’t heal
- Difficulty moving your jaw
- Red or white patches on the lining of your mouth – these are common and are very rarely cancerous, but they can sometimes turn into cancer, so it’s worth seeing a specialist if you have them
Diagnosis of Oral Cancer
Biopsy
The main methods used to carry out a biopsy in cases of suspected oral cancer are:
- An incision or punch biopsy
- A fine needle aspiration with cytology
- A nasendoscopy
- A panendoscopy
Further tests
Tests you may have include:
- An X-ray
- An ultrasound scan
- A magnetic roesonance imaging (MRI) scan
- A computerised tomography (CT) scan
- A positron emission tomography (PET) scan
Staging and grading
Staging is a measure of how far the cancer has spread. The TNM system of staging is used for staging mouth cancer:
- T – relates to the size of the tumour (also called the primary cancer) in the mouth; T1 is the smallest and T4 is the largest or most deeply invasive
- N – is used to show whether there are secondaries (metastases) in the neck lymph glands; N0 means none have been found during examination or on scans, and N1, N2 and N3 indicate the extent of neck secondaries
- M – refers to whether there are secondaries elsewhere in the body
Treatment of Oral Cancer
Treatment for oral cancer depends on your cancer’s location and stage, as well as your overall health and personal preferences. You may have just one type of treatment, or you may undergo a combination of cancer treatments. Treatment options include surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Discuss your options with your doctor.
Surgery
Surgery for oral cancer may include:
- Surgery to remove the tumor.
- Surgery to remove cancer that has spread to the neck.
- Neck dissection surgery will leave a scar on your neck. It won’t affect your body’s ability to fight infections in the future.
- Surgery to reconstruct the mouth.
Radiation therapy
Chemotherapy
Targeted drug therapy
- Cetuximab (Erbitux)
Exercise
Massage therapy
Relaxation
Acupuncture
Related Articles:
Esophageal Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Thyroid Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Vaginal Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Rectal Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Testicular Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Vulvar Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Gallbladder Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Pancreatic Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Case Seeking Cancer Screenings Heads To Trial
Solid Organ Transplant Patients At Higher Cancer Death Risk
A Sort Of Prostate Cancer Treatment May Upsurge Probabilities Of Alzheimer’s
Ovarian Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Alkaline Diet Helping In Cancer and Other Syndromes
By : Natural Health News




