What’s the Best Way to Control Atrial Fibrillation?
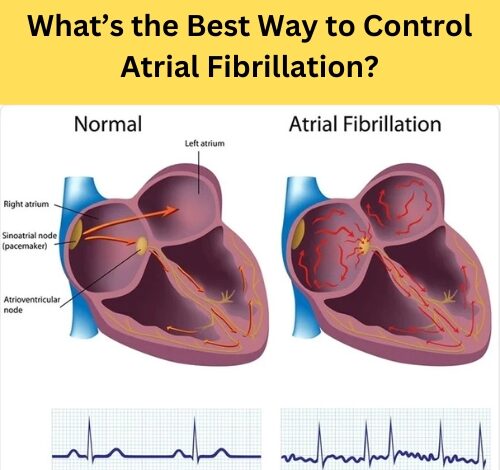
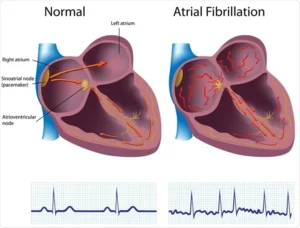
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is one of the most common heart rhythm disorders, affecting millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the heart’s upper chambers (atria) beat irregularly, leading to an increased risk of stroke, heart failure, and other cardiovascular complications. Managing AFib effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, medications, and, in some cases, medical procedures. The best ways to control atrial fibrillation and maintain a healthy heart.
What is Atrial Fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a common heart rhythm disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the upper chambers of the heart (atria) beat irregularly and out of sync with the lower chambers (ventricles). This irregular heartbeat can lead to complications such as blood clots, stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related issues.
Related articles: Fighting Atrial Fibrillation Naturally: 5 Tips to Get Started
Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
Several factors can contribute to the development of Atrial Fibrillation, including:
- Heart Conditions: High blood pressure, coronary artery disease, heart valve issues, and congenital heart defects can increase the risk.
- Chronic Diseases: Diabetes, thyroid disorders, and sleep apnea are known risk factors.
- Lifestyle Factors: Excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, high caffeine intake, and obesity can trigger AFib episodes.
- Aging: The risk of developing Atrial Fibrillation increases with age, particularly in individuals over 60.
- Genetics: A family history of Atrial Fibrillation may predispose some individuals to the condition.
Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation
AFib symptoms can vary widely among individuals. Some common symptoms include:
- Palpitations or a rapid, irregular heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fatigue and weakness
- Chest pain or discomfort (seek medical attention immediately if severe)
Some individuals may experience no symptoms, making early detection more challenging.
Related articles: Benefits of Heart-Healthy Diet Treatment for Atrial Fibrillation
Risk Factors for Atrial Fibrillation
Several factors increase the risk of developing Atrial Fibrillation, including:
- High blood pressure
- Heart disease
- Obesity
- Sleep apnea
- Diabetes
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Thyroid disorders
- Family history
Best Ways to Control Atrial Fibrillation
1. Lifestyle Modifications
One of the most effective ways to manage Atrial Fibrillation is by adopting heart-healthy lifestyle changes. These include:
Related articles: Best 6 Natural Treatment for Atrial Fibrillation
- Diet and Nutrition A balanced diet plays a crucial role in heart health. Consider the following dietary habits:
- Eat more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Reduce salt intake to help manage blood pressure.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol, as they can trigger Atrial Fibrillation episodes.
- Increase omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts to promote heart function.
- Regular Exercise Engaging in moderate-intensity exercise can improve cardiovascular health. Activities such as walking, cycling, and swimming help maintain a healthy weight and reduce stress. However, excessive or high-intensity workouts may trigger AFib episodes, so consult a healthcare provider before starting a new exercise regimen.
Related articles: 9 Helpful Ingredients for Atrial Fibrillation Permanent Cure Naturally
- Weight Management Obesity is a significant risk factor for Atrial Fibrillation. Losing excess weight through a combination of diet and exercise can help reduce Atrial Fibrillation episodes and improve overall heart function.
- Stress Management Chronic stress and anxiety can contribute to irregular heart rhythms. Stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help prevent AFib episodes.
- Sleep Optimization Sleep apnea is closely linked to Atrial Fibrillation. Proper diagnosis and treatment, such as using a CPAP machine, can significantly reduce the risk of Atrial Fibrillation -related complications.
2. Medications for Atrial Fibrillation
Medications play a vital role in controlling Atrial Fibrillation. The primary goals of medication therapy are to regulate heart rate, restore normal rhythm, and prevent blood clots.

- Rate Control Medications These drugs help slow the heart rate and include:
- Beta-blockers (e.g., metoprolol, atenolol)
- Calcium channel blockers (e.g., diltiazem, verapamil)
- Digoxin (used less frequently)
- Rhythm Control Medications Also known as antiarrhythmic drugs, these medications help maintain a normal heart rhythm:
- Amiodarone
- Flecainide
- Sotalol
- Dofetilide
- Blood Thinners (Anticoagulants) Atrial Fibrillation increases the risk of stroke due to the formation of blood clots in the atria. Anticoagulants help prevent clots from forming and include:
- Warfarin (requires regular blood monitoring)
- Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) like apixaban, rivaroxaban, and dabigatran
3. Medical Procedures for Atrial Fibrillation
For patients who do not respond to medications or lifestyle changes, medical procedures may be necessary.
- Cardioversion Cardioversion is a procedure that restores normal heart rhythm using electrical shocks or medication. It is often performed for patients with persistent Atrial Fibrillation.
- Catheter Ablation Catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that targets and destroys abnormal heart tissue responsible for Atrial Fibrillation. It is an effective treatment for patients who experience frequent or severe Atrial Fibrillation episodes.
- Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation For certain patients, especially those with slow heart rates or other electrical conduction issues, a pacemaker may be implanted. In AV node ablation, the connection between the atria and ventricles is disrupted, requiring a pacemaker to regulate the heartbeat.
- Left Atrial Appendage Closure (LAAC) In patients at high risk of stroke who cannot take blood thinners, LAAC devices like the Watchman device help prevent clot formation in the left atrial appendage.
4. Monitoring and Regular Check-Ups
Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are essential for managing Atrial Fibrillation effectively. Monitoring may involve:
- Routine ECGs or Holter monitors to track heart rhythm.
- Blood tests to assess medication levels and underlying conditions.
- Wearable devices or smartwatches to detect irregular heartbeats.
Conclusion
The best way to control atrial fibrillation involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and, when necessary, medical procedures. A heart-healthy lifestyle, proper medication management, and regular medical monitoring can help individuals with Atrial Fibrillation lead healthier, more fulfilling lives. If you suspect you have Atrial Fibrillation or need help managing it, consult a healthcare professional for a personalized treatment plan.