Alopecia Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
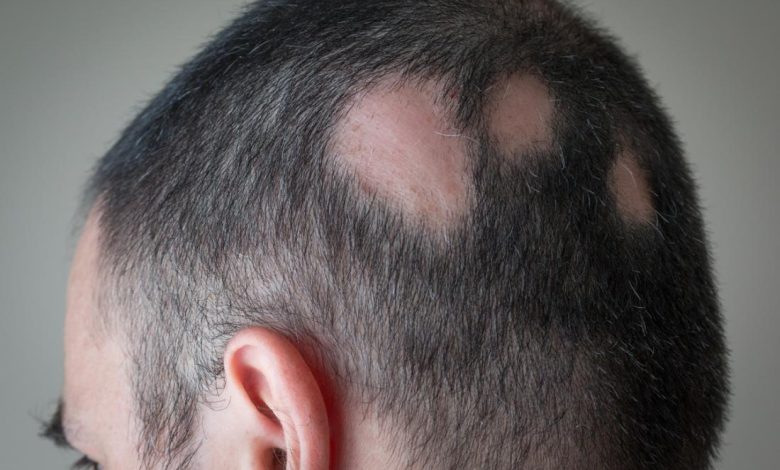
What Is Alopecia?
Commonly known as baldness and hair loss, alopecia is a common concern. It is a condition wherein a person experiences hair loss. Typically, alopecia affects your scalp. It causes a particular or even more patches of hair loss. It affects men and women both. For many people, alopecia resolves on its own without any treatment, however at times, hair loss caused by the condition is permanent.
What Are The Symptoms Of Alopecia?
Typically, hair loss tends to be the only prominent symptom of alopecia. Some individuals may even feel itching. In addition to this, alopecia starts as a particular or two to three patches of hair loss. Usually, the scalp is the main target of alopecia, causing hair loss. Though, it can also target your legs, arms, eyebrows and beard. These patches are mostly round in shape. They are smooth and can be of peach color. Sometimes, alopecia leads to complete loss of hair.
What causes alopecia?
A number of factors are considered to instigate alopecia, such as hair care habits, heredity, aging, hormonal changes, medications and underlying health conditions.
- Medical conditions known to root alopecia include:
1. Ringworm.
2. Illnesses or infections.
3. Thyroid disease.
4. Chronic iron deficiency.
5. Autoimmune disorder such as discoid lupus.
6. Anorexia.
7. Scalp fungus.
8. Anemia. - Few types of medications identified for triggering alopecia include:
1. Blood thinners.
2. Birth control pill.
3. High-dose vitamin A.
4. Blood pressure medications.
5. Anticancer chemotherapy.
6. Anabolic steroids.
7. Antidepressants.
8. Heart medications. - Some other conditions known to cause alopecia include:
1. Menopause.
2. Childbirth.
3. Poor nutrition.
4. Considerable weight loss.
5. Stress.
6. Pregnancy. - Hair care habits known for triggering alopecia include:
1. Chemical treatments.
2. Pulling or brushing hair when it’s wet.
3. Hair dyes.
4. Intense heat from heating irons.
5. Excessive shampooing.
What Are The Risk Factors Of Alopecia?
Below mentioned factors increases the risk of developing alopecia:
- Poor nutrition.
- Menopause.
- Illness.
- Family history.
- Age.
- Pregnancy.
- Improper hair maintenance.
- Stress.
How Is Alopecia Diagnosed?
A thorough examination of the affected scalp can help your dermatologist determine alopecia. In case the patch is expanding, he or she will pull out a sample of some hair in order to examine under a microscope. In few cases, the doctor will conduct skin biopsy in order to ascertain the condition.
How Is Alopecia Treated?
Treating the causal condition leading alopecia can help restore the growth of hair. However, finasteride (proscar) and minoxidil (rogaine) are the two drugs that have been recently introduce. The two are known to promote your hair growth affected by alopecia.
Prevention:
Of course, few factors known for causing the condition are unpreventable, for example menopause, age and heredity. Thankfully, there are certain ways one can follow to minimize the chances of alopecia. For example:
- Avoid using blow-dryers, curling or flat irons as much as possible. Such are known to dry out and damage your hair.
- Do not brush your hair when wet.
- Limit the use of harmful bleach and hair dyes.
- Shampoo your hair twice a weak only.
By : Natural Health News




