Arteriovenous Fistula Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
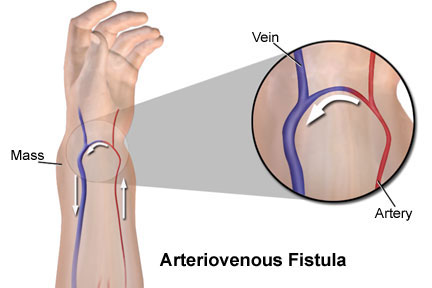
What Is Arteriovenous Fistula?
An arteriovenous fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway between an artery and a vein.
It may be congenital, surgically created for hemodialysis treatments, or acquired due to pathologic process, such as trauma or erosion of an arterial aneurysm.
With an arteriovenous fistula, blood flows directly from an artery into a vein, bypassing some capillaries. When this happens, tissues below the bypassed capillaries receive a diminished blood supply.
A large untreated arteriovenous fistula can lead to serious complications.
These include:
- Heart failure.
Since blood flows more quickly through an arteriovenous fistula than it would if the blood flowed through a normal course of arteries, capillaries and veins, the heart pumps harder to compensate for the drop in blood pressure.
This can weaken the heart muscle leading to heart failure. - Blood clots
Can lead to deep vein thrombosis in the legs. - Leg pain.
- Bleeding.
Arteriovenous malformations may lead to bleeding, including into the gastrointestinal system.
Causes Of Arteriovenous Fistulas:
Causes Of Arteriovenous Fistulas Include:
- Congenital (developmental defect)
- Rupture of arterial aneurysm into an adjacent vein
- Penetrating injuries
- Inflammatory necrosis of adjacent vessels
- Intentionally created (for example, Cimino fistula as vascular access for hemodialysis)
- Cardiac catheterization.
- Injuries that pierce the skin. .
- Being born with an arteriovenous fistula.
- Genetic conditions.
- hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
- Surgical creation (AV fistula procedure).
Symptoms Of Arteriovenous Fistulas:
Arteriovenous fistula signs and symptoms may include:
- Purplish, bulging veins that you can see through your skin, similar to varicose veins
- Swelling in the arms or legs
- Decreased blood pressure
- Fatigue
- Heart failure
- Blueness of the skin
- Clubbing of fingers
- Coughing up blood
Diagnosis Of Arteriovenous Fistula:
The following tests and exams help in the diagnosis of arteriovenous fistula:
- Duplex ultrasound.
A duplex ultrasound can estimate how fast blood flows by measuring the rate of change in its pitch (frequency). - Computerized tomography (CT) angiogram.
A CT angiogram allows the doctor to check your arteries to see if blood flow is bypassing the capillaries. - Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA).
This test allows the doctor to see the soft tissues in the body. It uses the same technique as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), but also includes the use of a special dye that helps create images of your blood vessels.
Treatment Of Arteriovenous Fistula:
The following treatment options are available:
- Ultrasound-guided compression.
- Catheter embolization.
- Surgery.
By : Natural Health News




