Bundle Branch Block Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Bundle Branch Block?
A bundle branch block is a defect of the bundle branches or fascicles in the electrical conduction system of the heart.
It is a condition in which there’s a delay or obstruction along the pathway that electrical impulses travel to make the heart beat.
The delay or blockage may occur on the pathway that sends electrical impulses to the left or the right side of the bottom chambers (ventricles) of the heart.
Depending on the anatomical location of the defect which leads to a bundle branch block, the blocks are further classified into:
- Right bundle branch block
- Left bundle branch block
There’s no specific treatment for bundle branch block itself. However, any underlying health condition that caused bundle branch block, such as heart disease, will need to be treated.
The main complication of bundle branch block is a slow heart rate, which can sometimes cause fainting.
People who have a heart attack and develop a bundle branch block have a higher chance of complications, including sudden cardiac death, than do people who have heart attacks and don’t develop a bundle branch block.
Since bundle branch block affects the electrical activity of the heart, it can sometimes complicate the accurate diagnosis of other heart conditions, especially heart attacks, and lead to delays in proper management of those problems.
Causes Of Bundle Branch Block:
The underlying cause for bundle branch blocks may differ depending on whether the left or right bundle branch is affected.
It’s also possible that this condition can occur without any known underlying cause.
Specific causes may include:
- Left bundle branch block
Heart disease
Thickened, stiffened or weakened heart muscle (cardiomyopathy)
A viral or bacterial infection of the heart muscle (myocarditis)
High blood pressure (hypertension) - Right bundle branch block
A heart abnormality that’s present at birth (congenital) — such as atrial septal defect, a hole in the wall separating the upper chambers of the heart
A heart attack (myocardial infarction)
A viral or bacterial infection of the heart muscle (myocarditis)
High blood pressure (hypertension)
A blood clot in the lungs (pulmonary embolism)
Risk Factors Of Bundle Branch Block:
- Increasing age.
Bundle branch block is more common in older adults than in people who are middle-aged. - Underlying health problems.
People who have high blood pressure or heart disease are more likely to have bundle branch block than people without those conditions
Symptoms of bundle branch block:
In most cases, bundle branch block do not cause any symptoms.
However, in case it does, the following symptoms may be exhibited:
- Fainting (syncope)
- Feeling as if you’re going to faint (presyncope)
Diagnosis Of Bundle Branch Block:
Diagnostic tests for bundle branch block may include:
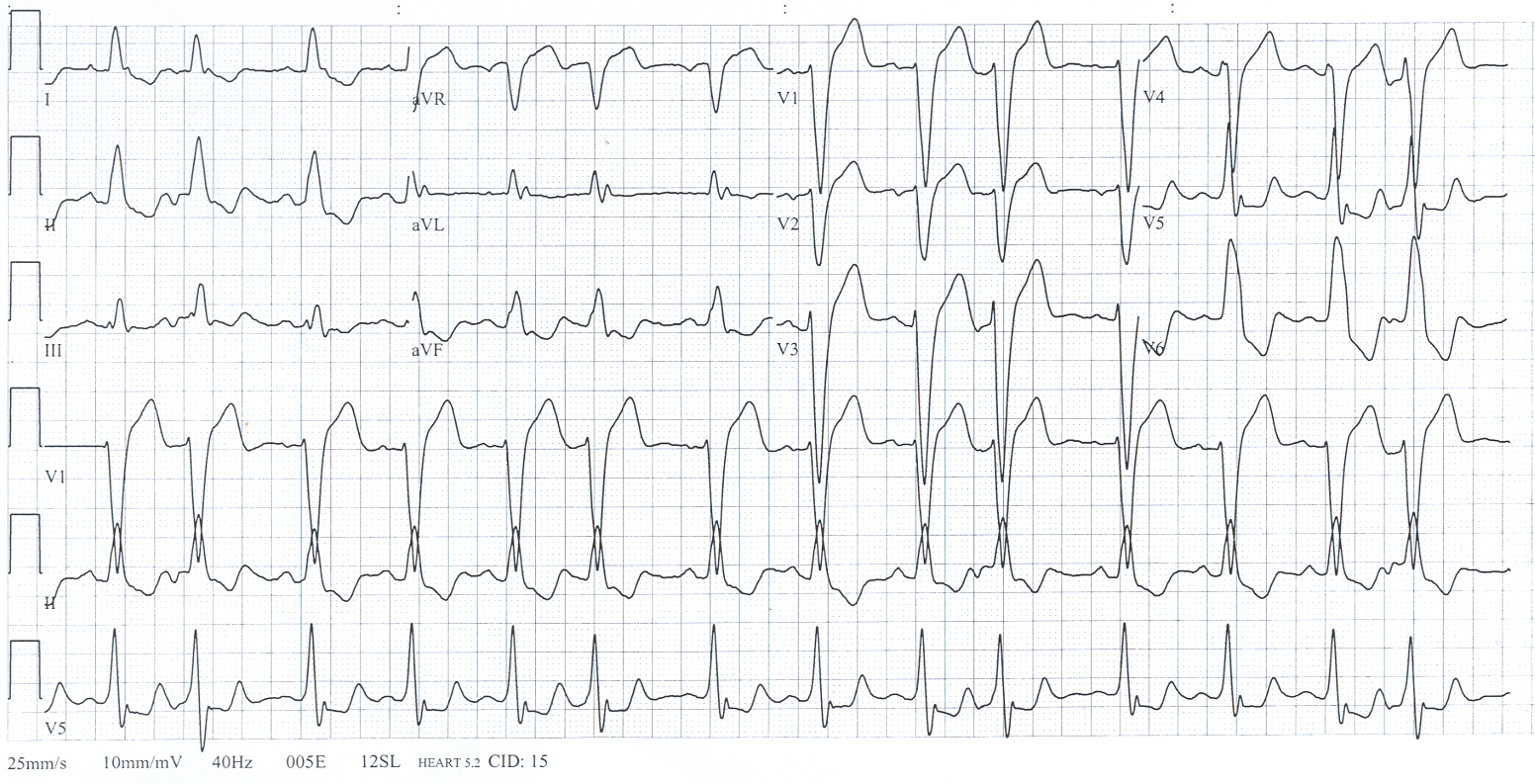
- Electrocardiogram.
Abnormalities may indicate the presence of bundle branch block, as well as which side is being affected. - Echocardiogram.
It can be used to pinpoint an underlying condition that caused the bundle branch block.
Treatment Of Bundle Branch Block:
Most people with bundle branch block are symptom-free and don’t need treatment
However, if you have an underlying heart condition causing bundle branch block, treatment of the underlying condition is recommended.
Depending on the signs and symptoms, the following additional treatments may be recommended:
- Pacemaker
- Cardiac resynchronization
By : Natural Health News