Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
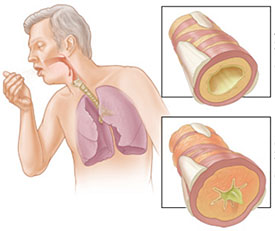
What is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease?
Also known as chronic obstructive lung disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or COPD is a type of obstructive lung disease characterized by poor air flow. It generally worsens over time.
Those suffering from chronic bronchitis may also suffer from COPD. The diagnosis of COPD is based on poor airflow as measured by lung function tests. In contrast to asthma, the airflow reduction does not improve significantly with the administration of a bronchodilator.
COPD is treatable. With proper management, most people with COPD can achieve good symptom control and quality of life, as well as reduced risk of other associated conditions.
COPD can be prevented by reducing exposure to known environmental risk factors. This includes decreasing rates of smoking and improving indoor and outdoor air quality
Causes of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease:
The primary cause of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease is tobacco smoking, with occupational exposure and pollution from indoor fires being significant causes in some countries (especially developing countries).
Other causes include:
- Air pollution
Indoor air pollution due to poorly ventilated cooking fires or use of biomass fuels - Occupational exposure
high levels of dust in coal mining
gold mining
cotton textile industry,
occupations involving cadmium and isocyanates
fumes from welding - Genetics
alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency - Airway obstruction
Emphysema
Chronic bronchitis
Symptoms of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease:
Symptoms of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease occur after the condition has already worsened.
The following symptoms are exhibited:
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activities
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
- Excess mucus in lungs
- Blueness of the lips or fingernail beds (cyanosis)
- Frequent respiratory infections
- Lack of energy
- Unintended weight loss (in later stages)
- Daily cough
- Sputum production, that may be clear, white, yellow or greenish
Diagnosis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease:
The following diagnostic tests are conducted:
- Pulmonary function tests.
Spirometry - Chest X-ray.
It may show emphysema
To rule out other lung problems or heart failure. - CT scan.
to help detect emphysema and help determine
to screen for lung cancer - Arterial blood gas analysis.
Treatment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease:
The following treatment options are available:
- Smoking cessation
- Medications
Inhalers (bronchodilators) to help open the airways
Inhaled or oral steroids to reduce lung inflammation
Anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce swelling in the airways
Certain long-term antibiotics - Lung therapy
Oxygen therapy
Pulmonary rehabilitation program - Surgery
Lung transplant
Lung volume reduction therapy
By : Natural Health News