Claudication Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Claudication?
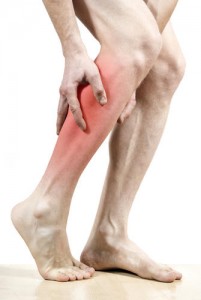
Claudication is the medical term used to refer to the impairment of walking that may occur due to some other disease. One such disease, which may cause claudication, is periphery artery disease.
Along with difficulty in walking, it also causes discomfort and is relieved by resting. The severity of the condition can range from mild to extremely severe.
Claudication is known to affect the feet, thighs, hips, buttocks, or arms.
The pain experienced due to claudication is usually detected when one exercises. Initially, it tends to go away once one rests. However, as claudication progresses, one may experience pain even while resting.
Fortunately, with prompt and proper treatment, one may lead a relatively normal life with claudication.
Causes Of Claudication:
Claudication is a symptom of Periphery artery disease, which is caused by atherosclerosis.
Peripheral artery disease is marked by damaged blood vessels due to atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis causes the arteries to become narrow and stiff. This damage to the vessel then causes claudication.
Other possible conditions associated with claudication may include:
- Spinal stenosis
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Certain musculoskeletal conditions
- Deep venous thrombosis
The following factors increase the risk of developing claudication:
- Smoking
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Obesity (a body mass index over 30)
- Diabetes
- Age older than 70 years
- A family history of atherosclerosis, peripheral artery disease or claudication
Symptoms Of Claudication:
Claudication is marked by the following signs and symptoms:
- Pain when exercising.
The pain may be located in the feet, calves, thighs, hips, arms or buttocks, depending on where the damage to the artery is. - Intermittent pain.
The pain initially comes and goes as less-strenuous activities are conducted. - Pain when at rest.
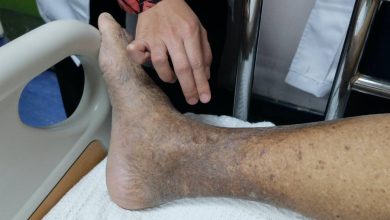
Eventually, as claudication progresses, pain is experienced even when resting. - Discolored skin or ulcerations.
If blood flow is severely reduced, toes or fingers may look bluish or feel cold to the touch.
Sores may develop sores on lower legs, feet, toes, arms or fingers. - An aching or burning feeling
- Weakness
Diagnosis Of Claudication:
In order to diagnose claudication, the following tests are conducted:
- Checking the pulses in the affected individual’s feet
- Ankle-brachial index to compare the blood pressure in the ankles to the blood pressure in the arms
- Doppler ultrasound, which monitors blood flow in the area affected
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computerized tomography (CT) angiography to show if your blood vessels are narrowed with plaque
Treatment Of Claudication:
The following treatment options help in relieving symptoms:
- Medications.
clopidogrel (Plavix)
dipyridamole (Persantine)
Ticlopidine.
cilostazol (Pletal) - Angioplasty.
- Vascular surgery.
By : Natural Health News