Cold Urticaria Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
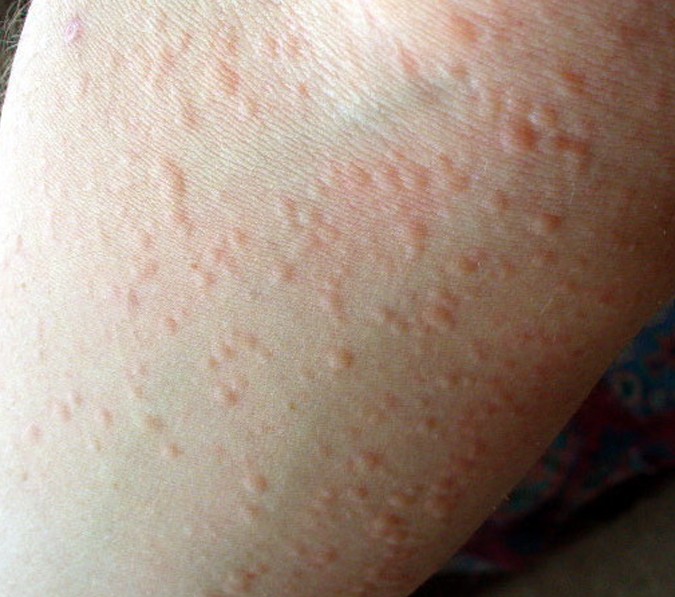
What Is Cold Urticaria?
Cold urticaria is a skin reaction to cold. In cold urticaria, hives appear on the skin after exposure to cold stimulus.
The severity of the symptoms may vary widely. It can range from minor reactions to cold to severe reactions. The most common cause of a whole body reaction is swimming in cold water. This in turn may cause low blood pressure, fainting, shock and even death.
This disorder, or perhaps two disorders with the same clinical manifestations, can be inherited (familial cold urticaria) or acquired (primary acquired cold urticaria).
The acquired form is most likely to occur between ages 18–25, although it can occur as early as 5 years old in some cases.
Causes Of Cold Urticaria:
Cold urticaria is a histamine reaction in response to cold stimuli, including a drastic drop in temperature, cold air, and cold water.
There are many causes for it, most are idiopathic in nature (meaning they have no known cause). Some rare conditions can cause cold urticaria, and it can be useful to test for these conditions if the cold hives are in any way unusual.
Underlying conditions that have been associated with secondary cold urticaria include:
- cryoglobulinemia
- chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- lymph sarcoma
- chickenpox (varicella)
- viral hepatitis
- Infectious mononucleosis (glandular fever)
Although anyone can develop cold urticaria, the following individuals are more likely to develop it:
- Being a child or young adult
- Those who recently had an infection.
Pneumonia has been linked to cold urticaria. - Those having underlying health condition.
Secondary acquired cold urticaria can be caused by an underlying health problem, such as hepatitis or cancer. - Having certain inherited traits
Symptoms Of Cold Urticaria:
The following signs and symptoms are exhibited:
- Temporary reddish, itchy welts (hives) on the area of skin that was exposed to cold
- A worsening of the reaction as the skin warms
- Swelling of hands when holding cold objects
- Swelling of lips and throat when consuming cold food or drink
Diagnosis Of Cold Urticaria:
Diagnosis is typically obtained by an allergist or other licensed practitioner performing a cold test. During the cold test, a piece of ice is held against the forearm, typically for 2–3 minutes. A positive result is a specific looking mark of raised red hives. The hives may be the shape of the ice, or it may radiate from the contact area of the ice.
If the doctor suspects the cause to be some underlying condition, further blood tests may be conducted to find the root cause.
Treatment Of Cold Urticaria:
Although there is no definite cure for cold urticaria, treatment may help in relieving symptoms.
Treatment includes taking different medications.
- Antihistamines.
Fexofenadine (Allegra)
Desloratadine (Clarinex). - Cyproheptadine.
- Doxepin (Silenor).
- Omalizumab (Xolair).
Related Articles:
Bursitis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Folliculitis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Carcinoid Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Buerger’s Disease Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Shingles Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Chilblains Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Cradle Cap Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Contact Dermatitis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Henoch Schonlein Purpura (HSP) Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Soft Tissue Sarcoma Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Pilonidal Cyst Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
By : Natural Health News




