Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What is Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis?
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) is a non inflammatory spondyloarthropathy of the spine. Spondyloarthropathy refers to any joint disease of the vertebral column.
It is also defined as calcification of ligaments attached to the spine. In people with dextrocardia and situs inversus this calcification occurs on the left side
Characterized by spiny ankylosis (stiffness of the spine) and esthesopathy, it most commonly affects the thoracic spine but can affect the entire spine as well. The disc spaces, facet and sacroiliac joints are generally not affected.
DISH may not cause any symptoms in the affected individual and therefore require no treatment. However if symptoms, which include pain and stiffness in the back, do occur, treatment may be sought.
Affected areas may include lower back, neck, shoulders, elbows, knees and heels. It is generally considered to be a degenerative arthritis or osteoarthritis.
Causes of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis:
The underlying cause of DISH is yet unknown. Research in this domain is still ongoing.
Possible factors which may play a role may include:
- Mechanical factors
- Diet
- Long term use of antidepressants
- Having metabolic syndrome
While there is a correlation between these factors, no causal relationship has been established so far.
Risk Factors of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis:
- Being older than 60
- Being a male
- Having conditions including diabetes, hyperinsulinemia, prediabetes and obesity.
Although the disease itself is not fatal, some associated complications may lead to death. These include:
- Paralysis
- Dysphagia (the inability to swallow)
- Pulmonary infections
- Spinal fracture
Symptoms of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis:
Dish may or may not cause any symptoms.
In case of exhibition of symptoms, it may include the following:
- Spinal stiffness on forwards flexion and back extension
- Mild to moderate pain
- Dysphagia or difficulty in swallowing may occur
- Hoarse voice
- Loss in range of motion
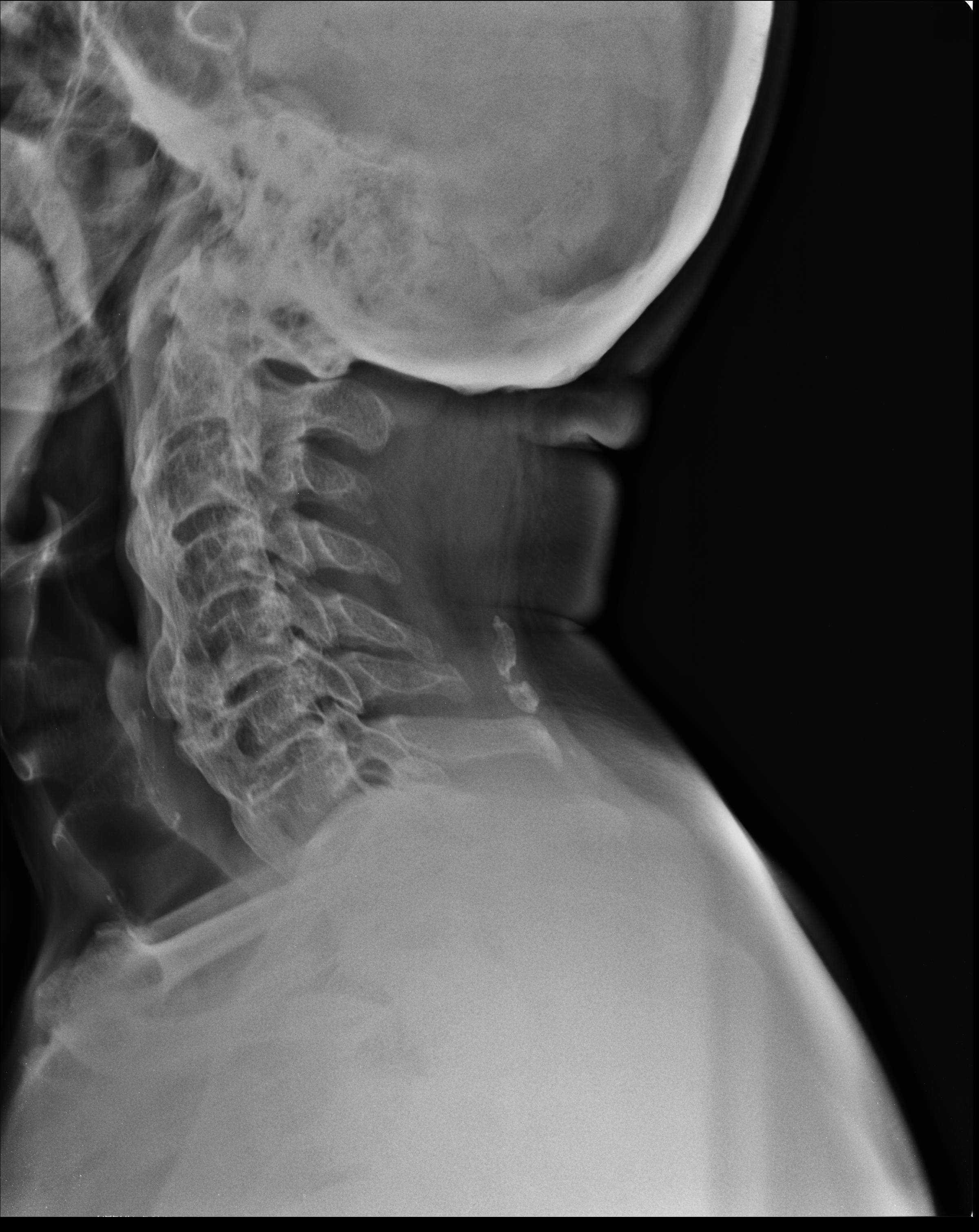
Diagnosis of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis:
DISH can be diagnosed via:
- Physical examination, which may involve pressing the spine to detect for abnormalities
- Imaging tests
MRI
CT scan
X-rays
Treatment of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis:
The following treatment options are available:
- Medications, to relieve pain
Acetaminophen
ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin)
naproxen (Aleve), - Physical therapy, to treat stiffness
- Surgery
To relieve pressure on the spinal cord
Removing bone spurs in case of difficulty in swallowing
By : Natural Health News




