Ehrlichiosis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Ehrlichiosis?
Ehrlichiosis is a tickborne bacterial infection, caused by bacteria of the family Anaplasmataceae, genera Ehrlichia and Anaplasma. These bacteria infect and kill white blood cells.
The signs and symptoms of ehrlichiosis range from mild body aches to severe fever and usually appear within a week or two of a tick bites.
If treated quickly with appropriate antibiotics, ehrlichiosis generally improves within a few days.
Without prompt treatment, ehrlichiosis can have serious effects.
Moreover, People with weakened immune systems are at an even higher risk of more-serious and potentially life-threatening consequences.
Serious complications of untreated infection include:
- Kidney failure
- Respiratory failure
- Heart failure
- Seizures
- Coma
Causes Of Ehrlichiosis:
Ehrlichiosis is caused by ehrlichia bacteria and is transmitted primarily by the Lone Star tick.
Ticks feed on blood, and during feeding, ticks that carry disease-producing bacteria can transmit the bacteria to a healthy host.
Being bitten by an infected tick is usually the cause of developing ehrlichiosis.
Before bacteria can be transmitted, a tick must be attached and feeding for at least 24 hours. An attached tick with a swollen appearance may have been feeding long enough to have transmitted bacteria.
Other possible modes of transmission include:
- Blood transfusion (from someone infected with ehrlichiosis)
- An infected mother can pass it on the fetus
- Direct contact with an infected, slaughtered animal
The Following Factors Increase The Risk Of Developing Ehrlichiosis:
- Being outdoors in warm weather.
- Living in or visiting an area with a high tick population.
- Being male.
Symptoms Of Ehrlichiosis:
Signs and symptoms may include:
- Mild fever
- Headache
- Chills
- Muscle aches
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Joint pain
- Confusion
- Rash
- Cough
- Diarrhea
- Fine pinhead-sized areas of bleeding in the skin (petechial rash)
- Flat red rash (maculopapular rash) (uncommon)
- General ill feeling (malaise)
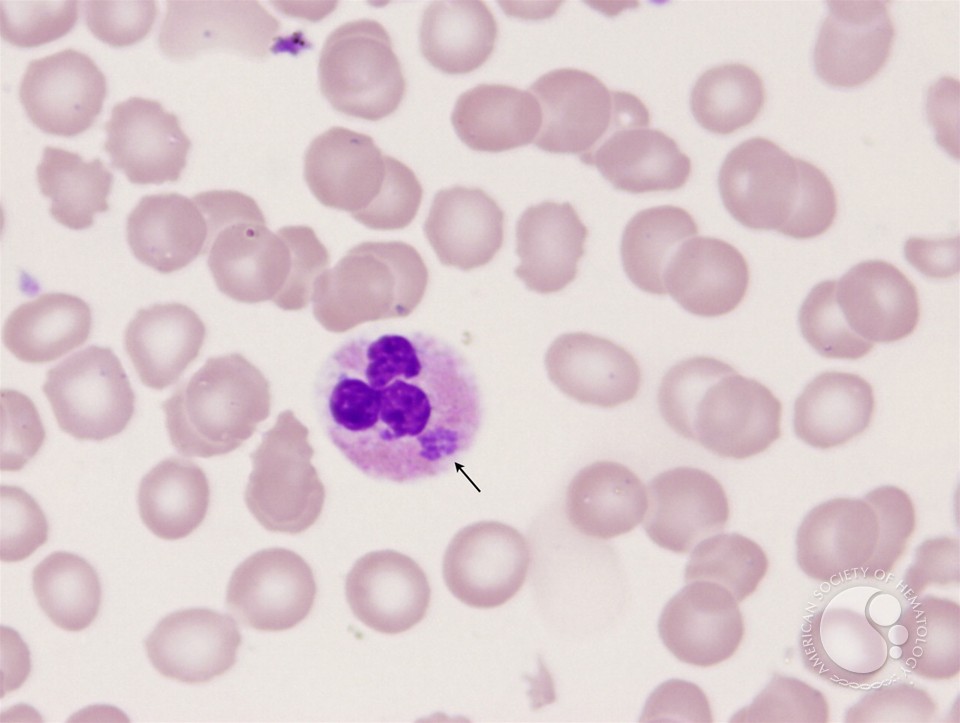
Diagnosis Of Ehrlichiosis:
The following tests help confirm the diagnosis:
- Blood test
If infected with ehrlichiosis, blood test will show:
Abnormal liver function
Low white blood cell count
Low platelet count
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test, to identify specific genes unique to ehrlichiosis.
- Indirect fluorescent antibody (IFA) test, to measure the amount of antibody to the bacteria present in the body
- Granulocyte stain
Treatment Of Ehrlichiosis:
Ehrlichiosis can be treated through medications.
Doxycycline and minocycline are the medications of choice. For people allergic to antibiotics of the tetracycline class, rifampin is an alternative.
Common measures to prevent tick bites include:
- Avoiding dense brush and long grasses when hiking
- Checking yourself for ticks and removing any that you find after being outside
- Not standing under trees or bushes
- Using insect repellent
- Wearing clothing to cover skin
By : Natural Health News




