Endocarditis Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
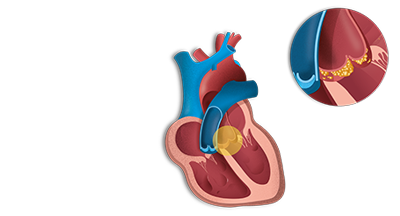
What is endocarditis?
Endocarditis, is characterized as the infection of endocardium. Endocardium is basically the inner lining of a heart. The infection tends to develop when some germs or bacteria from the other part of a body, for example mouth, spread through the bloodstream, whilst attach to the damaged areas of a heart.
Moreover, if endocarditis is left untreated, it can destroy or damage the valves of your heart and may lead to some serious complications. Its treatment include antibiotics, however, surgery is also an option in rare cases. The condition is exceptional in individuals those have healthy hearts. People, whose heart valves are damaged, are more likely to experience endocarditis.
What are the symptoms of endocarditis?
The condition can either develop suddenly or slowly, depending upon:
- Whether you have any causal heart problems .
- What’s exactly triggering the infection.
Its symptoms tend to differ, however may include:
- Persistent cough.
- Paleness.
- Breathing difficulties.
- Fever and chills.
- Night sweats.
- Aching muscles and joints.
- Fatigue.
- Changed or new heart murmur.
- Blood in urine.
- Weight loss.
- Swelling in abdomen, legs or feet.
- Osler’s nodes.
- Petechiae.
- Tenderness in spleen.
What causes endocarditis?
The condition occurs after the germs or bacteria enters the bloodstream; passing through the heart and later attaching to its damaged tissue and abnormal valves. Moreover, bacteria are responsible for triggering most cases. Fungi plus other microorganisms can also cause endocarditis. At times, that particular offending organism is among the numerous bacteria present in your throat, mouth or other body parts. It can enter the bloodstream through:
- Needles or catheters.
- Oral activities.
- An infection.
- Some dental procedures.
What are the risk factors of endocarditis?
Fortunately, people with healthy hearts are unlikely to experience the condition. However, the germ responsible for leading the infection sticks and multiplies particularly in surgically implanted or damaged heart valves. Individuals those have the following concerns are more likely to develop endocarditis:
- Congenital heart defects.
- Artificial/damaged heart valves.
- History of the condition.
- History of using intravenous illegal drug.
What are the possible complications of endocarditis?
Few serious complications associated with endocarditis include:
- Organ damage.
- Stroke.
- Heart failure.
- Infections in other body parts.
How is endocarditis diagnosed?
Physical symptoms (fever) and medical history of the patient can help a doctor diagnose endocarditis. Through a stethoscope, the doctor will hear the new or changed heart murmur. In order to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor can suggest:
- Blood tests.
- ECG.
- Transesophageal echocardiogram.
- Chest X-ray.
- CT scan or MRI.
How is endocarditis treated?
If you are diagnosed with endocarditis, your doctor will prescribe intravenous antibiotics. If the infection has cause damage to the heart valve, then surgery is needed.
Prevention:
- Practicing good hygiene is very important.
- Avoid procedures known to cause skin infections for example tattoos or piercing.
- Pay attention to the dental health.
By : Natural Health News




