Eosinophilic Esophagitis Causes, Symptoms, Diangosis and Treatment
What Is Eosinophilic Esophagitis?
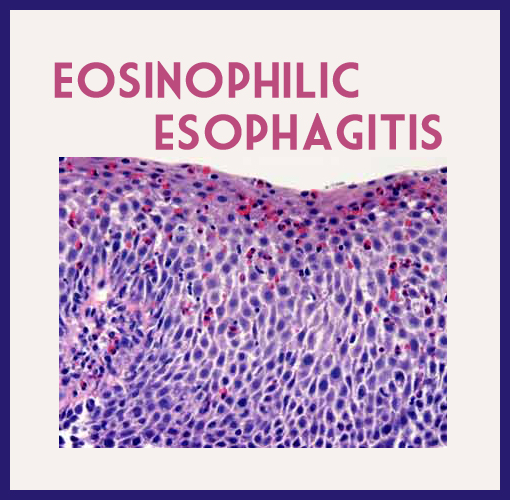
Eosinophilic esophagitis is an allergic inflammatory condition of the esophagus which involves eosinophil (a type of white blood cell). Although it largely affects children, it can occur in children too.
As eosinophil builds up in the lining of the esophagus, this causes stiffening and inflammation of the esophagus. This buildup can injure the esophageal tissue thereby causing symptoms.
Reflux of stomach acid contents into the esophagus can also cause eosinophils as well as inflammation in the esophagus. It is more common in males than females and may run in the family.
One of the major causes of digestive system illness, eosinophilic esophagitis is still a subject of research in the domain of diagnoses and treatment. The treatment may consist of removal of known or suspected triggers and medication to suppress the immune response.
Causes Of Eosinophilic Esophagitis:
Cause of eosinophilic esophagitis is not fully understood. However, researchers believe that is caused when the esophagus reacts to allergens. Such allergens may include food or pollen.
Moreover, in eosinophilic esophagitis, affected eosinophils multiply in the esophagus thereby causing a buildup which causes stiffening of the esophagus.
This multiplication may be due to a protein made by eosinophils which cause inflammation. This leads to the exhibition of various symptoms.
Other factors include:
- Food allergies
- Environmental allergies
- Asthma
- Atopic dermatitis
- Chronic respiratory disease
- Eczema
- Genetic predisposition
Possible Risk Factors Include:
- Being a male
- Living in a dry climate
- Being a child
- Having a family history of the disease
Symptoms Of Eosinophilic Esophagitis:
Symptoms differ in adults and children.
In adults, the following symptoms are exhibited:
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Food impaction
- Chest pain
- Persistent heartburn
- Upper abdominal pain
- No response to gastroesophageal reflux disease medication
- Backflow of undigested food (regurgitation)
In children the following symptoms may occur:
- Difficulty feeding
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Food impaction
- No response to GERD medication
- poor growth
- malnutrition
- weight loss
Diagnosis Of Eosinophilic Esophagitis:
The following tests are conducted in order to diagnose eosinophilic esophagitis:
- Upper endoscopy
- Biopsy.
- Blood tests, to look for higher than normal eosinophil counts or total immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels, suggesting allergy.
- Medication trials.
- Dietary treatment trials.
- Food-patch test.
Treatment Of Eosinophilic Esophagitis:
Treatment may involve the following:
- Dietary therapy
- Medication
- Dilation
- Experimental therapy
By : Natural Health News