Esophageal Varices Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
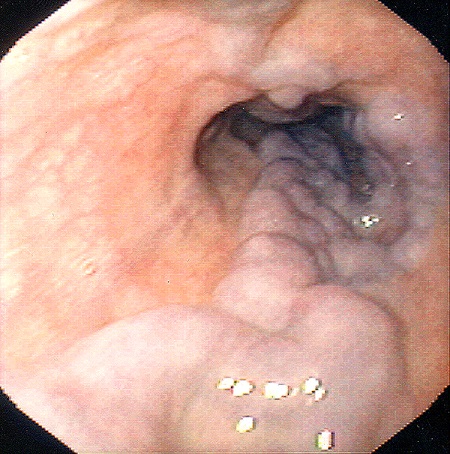
What Are Esophageal Varices?
These are the abnormal and enlarged veins in the lower part of your esophagus. Basically, esophagus is a tube which joins the throats to the stomach. The condition commonly occurs in individuals those suffering from advance liver diseases.
In addition to the characteristics of esophageal varices, it arises when the smooth flow of blood to your liver is disturbed. This occurs due to a clot or scar tissue present in your liver. The blood then seeks other means to flow, such as tiny blood vessels around the blockages. Since, these are not intended for heavy flow of blood, thus, this can lead to leakage. Moreover, these blood vessels can even rupture, sourcing severe bleeding. Several medical procedures and drugs are used to avert and halt the bleeding from the condition.
What Are The Symptoms Of Esophageal Varices?
Often, esophageal varices source no indications until they bleed. Some common signs of bleeding esophageal varices are as follow:
- Bloody, tarry or black stools.
- Vomiting blood.
- Shock (serious cases).
The health care provider can doubt varices on the basis of the symptoms of liver disease, such as:
- Swollen spleen.
- Shrunken testicles.
- Yellow coloration of the eyes and skin.
- Spider nevi.
- Palmar erhthema.
- Ascites.
- Dupuytren’s contracture.
What Causes Esophageal Varices?
At times, it occurs due to the obstruction in the smooth blood flow to the liver. Usually, this obstruction is resulted due to a scar tissue present in the liver that is sourced by liver disease. In addition to this, blood flow to the liver starts to roll up, rising force within the portal vein. Portal veins are responsible for transporting the blood to the liver. Moreover, the pressure makes the blood find other pathways. The blood then travels through tiny veins, for example the ones present in the lower part of your esophagus. Since, these vessels are not intended to transmit blood, these with leak or rupture.
Triggers of esophageal varices are as follow:
- Cirrhosis.
- Thrombosis.
- Parasitic infection.
- Budd-Chiari syndrome.
What Are The Risk Factors Of Esophageal Varices?
Even though, majority patients suffering from serious liver disease faces esophageal varices, yet many do not experience bleeding. Clearly, a person with varices will possibly bleed in case he or she has:
- Large varices.
- High portal vein pressure.
- Red marks on the varices.
- Liver failure or cirrhosis.
What Are The Complications Of Esophageal Varices?
Following are the complications of esophageal varices:
- Bleeding.
- Shock.
- Death.
How Is Esophageal Varices Diagnosed?
Following tests can help detect esophageal varices:
- Endoscope exam.
- Imaging tests.
- Capsule endoscopy.
How Is Esophageal Varices Treated?
Esophageal varices that bleed are dangerous. Therefore, the treatment aims to avert or halt the bleeding. A number of treatment options are reviewed to stop the bleeding.
To prevent esophageal varices, it is advice to quit alcohol, consume a balanced diet, shed the extra pounds and maintain healthy weight.
By : Natural Health News




