Factor V Leiden Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Factor V Leiden?
Factor V Leiden is a genetic disorder of blood clotting. Factor V Leiden is a variant (mutated form) of human factor V (one of several substances that help blood clot) that causes an increase in blood clotting (hypercoagulability)
In this disorder, the Leiden variant of factor V cannot be inactivated by the anticoagulant protein so clotting is encouraged.
People with factor V Leiden have a higher than average risk of developing a type of blood clot called a deep venous thrombosis (DVT).
DVTs occur most often in the legs, although they can also occur in other parts of the body, including the brain, eyes, liver, and kidneys.
It also increases the risk that clots will break away from their original site and travel through the bloodstream. These clots can lodge in the lungs, where they are known as pulmonary emboli.
The factor V Leiden mutation is associated with a slightly increased risk of miscarriage.
Moreover, factor V Leiden mutation may also increase the risk of other complications during pregnancy, including pregnancy-induced high blood pressure (preeclampsia), slow fetal growth, and early separation of the placenta from the uterine wall (placental abruption).
However, the association between the factor V Leiden mutation and these complications has not been confirmed.
Cause Of Factor V Leiden:
Normally, Factor V works with other proteins and enzymes to create the substances the body needs to regulate clotting.
Factor V Leiden makes it harder for anti-clotting proteins to break up factor V. This keeps factor V in the blood longer and increases the chance of clotting.
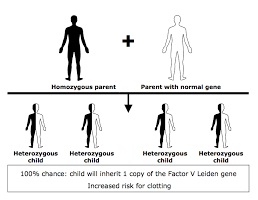
Having factor V Leiden is due to hereditary reasons. Those affected have either one or two copies of the defective gene (zygous).
Inheriting two genes highly increases the risk of developing blood clots.
Symptoms Of Factor V Leiden:
Most people with factor V Leiden do not exhibit any signs and symptoms. In case they do, the following are exhibited:
- Development of blood clot
- Clot development in deep vein
- Pain
- Swelling
- Redness
- Development of a clot closer to the surface of the skin
- Tenderness
- Pain
- Clot which travels to the lung
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Tachycardia
Diangosis Of factor V Leiden:
The following tests may be conducted to detect the presence of factor V Leiden:
- Activated protein C resistance test.
- Genetic test
Treatment Of factor V Leiden:
No treatment is required if there is an absence of a blood clot. In case of a blood clot, blood thinners may be prescribed.
Possible blood thinners may include:
- Heparin
- Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven).
- Dabigatran (Pradaxa)
- Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
- Apixaban (Eliquis)
By : Natural Health News