Gigantism Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
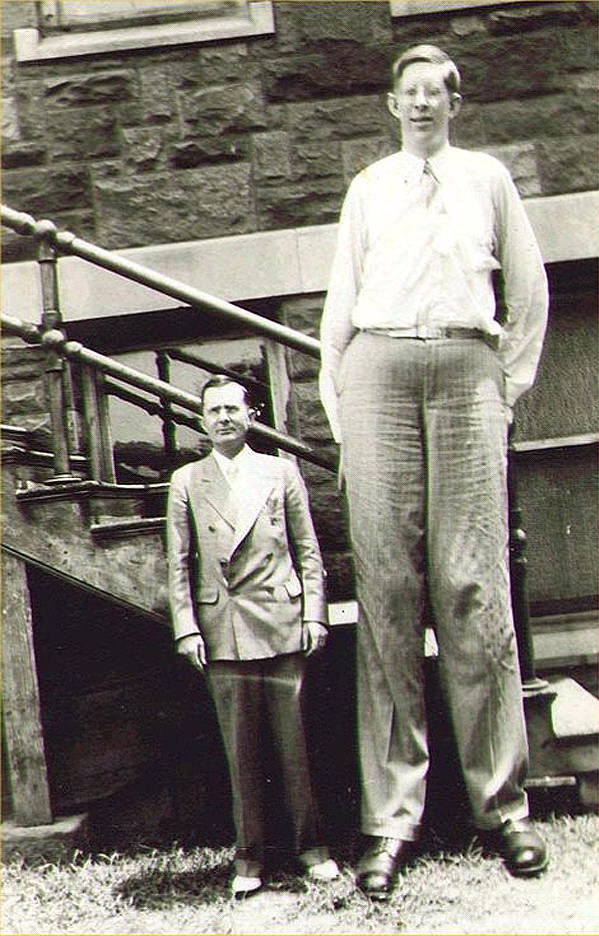

What Is Gigantism?
It is a rare condition wherein children affected by it experiences abnormal growth. When the body of a child makes abnormal amount of growth hormone, gigantism arises. Diagnosing it at an early stage is important, as prompt treatment pursued, based on early diagnosis can help slow down or stop the changes that tend to make the growth of a child larger than normal. Though, gigantism can be difficult to identify for the parents, as initially, its symptoms might look like the usual growth spurts of childhood.
What Are The Symptoms Of Gigantism?
A child with gigantism tends grow in height, organs and muscles. Such ‘excessive’ growth results in the child to turn unusually large as compared to other children of his/her age. Few other symptoms of gigantism are:
- Headache.
- Difficulty with peripheral vision or double vision.
- Delayed puberty.
- Frontal bossing.
- Prominent jaw.
- Irregular periods.
- Increased sweating.
- Gaps between the teeth.
- Weakness.
- Release of breast milk.
- Sleep problems.
- Large feet and hands.
- Thick toes and fingers.
- Double vision.
What Causes Gigantism?
Almost, in all cases of gigantism, pituitary gland tumor is the cause. Pituitary gland is a pea-sized gland, positioned at the bottom of the brain. The gland is responsible for producing hormones which control various bodily functions. Few of which include:
- Sexual development.
- Temperature control.
- Urine production.
- Growth metabolism.
In case a tumor develops on pituitary gland, it results in the overproduction of growth hormone. Rarely, gigantism may occur due to the following:
- Carney complex.
- McCune-Albright syndrome.
- Neurofibromatosis.
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1.
What Are The Possible Complications Of Gigantism?
Even though, surgery can help restrict the production of growth hormone, yet it can lead to decrease levels of some other hormones produce by pituitary gland. This can cause the following complications:
- Hypothyroidism.
- Hypogonadism.
- Diabetes insipidus.
- Adrenal insufficiency.
How Is Gigantism Diagnosed?
During the visit, the doctor will conduct a though physical exam, whilst ask details regarding the symptoms of the child. The doctor can then suggest the following lab tests:
- Thyroid hormone.
- Testosterone (boys).
- Increased growth factor-I
- Prolactin.
- Growth hormone suppression test.
- Estradiol (girls).
- Cortisol.
In order to test for a pituitary tumor, the doctor can suggest imaging tests for example MRI or CT scan of the head.
How Is Gigantism Treated?
In order to treat pituitary tumors with sharp borders, the doctor can recommend surgery. However when surgery fails to remove the tumor entirely, the doctor can then prescribe medicines in order to lessen or block the release of growth hormone.
What Is The Prognosis Of Gigantism?
Often, pituitary surgery is effective enough to restrict the production of growth hormone. Treatment pursued at an initial stage can help reverse several changes rooted by excessive growth hormone.
By : Natural Health News