Glomerulonephritis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
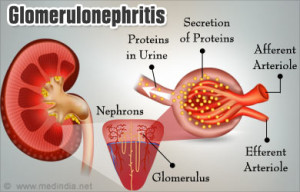
What Is Glomerulonephritis?
Glomerulonephritis, also known as glomerular nephritis, is a term used to refer to several kidney diseases (usually affecting both kidneys).
Many of the diseases are characterised by inflammation either of the glomeruli or small blood vessels in the kidneys, hence the name, but not all diseases necessarily have an inflammatory component.
If glomerulonephritis occurs on its own, it’s known as primary glomerulonephritis.
If another disease, such as lupus or diabetes, is the cause, it’s called secondary glomerulonephritis.
Causes of Glomerulonephritis:
Sometimes the cause of glomerulonephritis is unknown.
However, many conditions can lead to the development of glomerulonephritis.
- Infections
- Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis.
- Glomerulonephritis may develop a week or two after recovery from a strep throat infection or, rarely, a skin infection (impetigo).
- To fight the infection, body produces extra antibodies that may eventually settle in the glomeruli, causing inflammation.
- Bacterial endocarditis.
- Bacteria occasionally can spread through the bloodstream and lodge in the heart, causing an infection of one or more of the heart valves.
- Viral infections.
- Viral infections, such as the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B and hepatitis C, may trigger glomerulonephritis.
- Immune diseases
- Goodpasture’s syndrome.
- IgA nephropathy.
- Vasculitis
- This form of vasculitis affects small and medium blood vessels in many parts of the body, such as your heart, kidneys and intestines.
- Wegener’s granulomatosis.This form of vasculitis affects small and medium blood vessels in your lungs, upper airways and kidneys.
The following conditions can cause scarring of the glomeruli:
- High blood pressure.
- Diabetic kidney disease.
- Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.
Symptoms of Glomerulonephritis:
The following symptoms are exhibited by the Glomerulonephritis:
- Pink or cola-colored urine from red blood cells in your urine (hematuria)
- Foamy urine due to excess protein (proteinuria)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Fluid retention (edema) with swelling evident in your face, hands, feet and abdomen
- Fatigue from anemia or kidney failure
Diagnosis of Glomerulonephritis:
Glomerulonephritis is diagnosed via the following:
- Urine examination
- Blood tests investigating the cause, including FBC, inflammatory markers and special tests including (ASLO, ANCA, Anti-GBM, Complement levels, Antinuclear antibodies
- Imaging tests
- Biopsy of the kidney
Treatment of Glomerulonephritis:
Treatment of glomerulonephritis and your outcome depend on:
- Whether the individual has an acute or chronic form of the disease
- The underlying cause
- The type and severity of the signs and symptoms
The goal of the treatment is to protect kidneys from further damage:
- Medication for high blood pressure
- Diuretics
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers
- Treating the underlying cause
- Therapies
By : Natural Health News




