Graves’ Disease Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
What is Graves’ disease?
The immune system disorder, Graves’ disease consequents the abnormal growth of thyroid hormone, a condition called hyperthyroidism. Generally, certain disorders are known to cause hyperthyroidism, though Graves’ disease tends to be a common trigger of hyperthyroidism. Graves’ disease can strike anyone, however it commonly affects women under 40 years of age. Its treatment aims to control the abnormal growth of thyroid hormones, whilst reducing the severity of its symptoms.
What are the symptoms of grave’s disease?
Few of its common symptoms include:
- Irritability or anxiety.
- Irregular or rapid heartbeat.
- Graves’ dermopathy.
- Slight tremor of the fingers or hands.
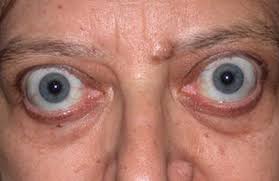
- Graves’ ophthalmopathy.
- Frequent bowel movements.
- Reduced libido or erectile dysfunction.
- Change in menstrual cycles.
- Heat sensitivity.
- Moist skin.
- Goiter.
- Considerable weight loss.
What causes Graves’ disease?
Clearly, thyroid gland tends to be a key organ of our endocrine system. It releases the useful hormones triiodothyronine and thyroxine. The hormones are responsible for controlling the metabolism of our body that leads in regulating our physical and mental energy levels.
Hyperthyroidism is a condition wherein the body turns producing abnormal levels of thyroid hormones. Graves’ disease tends to be a common trigger of hyperthyroidism. More specifically, because of the response of an overactive immune system, it leads your thyroid gland to make excessive levels of thyroid hormone.
What are the risk factors of Graves’ disease?
Any individual regardless of ages, genders or races can develop the condition, though few factors make you more likely to develop Graves’ disease, they are:
- If Graves’ disease runs in your family.
- If you are a female.
- If you are below the age of 40 years.
- Have any other autoimmune disorders.
- Have emotional stress.
- If you are pregnant.
What are the potential complications of Graves’ disease?
Potential complications associated with Graves’ disease include:
- Heart disorders.
- Pregnancy issues.
- Thyroid storm.
- Brittle bones
How is Graves’ disease diagnosed?
In order to diagnose the condition, the doctor can conduct or suggest the following:
- Physical exam.
- Blood sample.
- Radioactive iodine uptake.
- Ultrasound.
- Imaging tests.
How is Graves’ disease treated?
The treatment of Graves’ disease involves controlling the overactive thyroid. The doctor can prescribe beta-blockers in order to treat its symptoms, until hyperthyroidism gets controlled. Furthermore, the doctor can suggest any or more of the below mentioned options in order to treat hyperthyroidism.
- Surgery.
- Radioactive iodine.
- Antithyroid medications.
In case the doctor suggests surgery or radioactive iodine treatment, then the patient also needs to undergo replacement thyroid hormones for his or her entire life. The apparent reason is that such treatments tend to remove or destroy your gland.
Prevention:
Physical and mental well being is very important for the person suffering from Graves’ disease, thus:
- Eat a balanced diet.
- Do exercise for at least 25 minutes a day, regularly.
- Let go your stress.
- Quit smoking.
By : Natural Health News




