Guillain Barre Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Guillain Barre Syndrome?
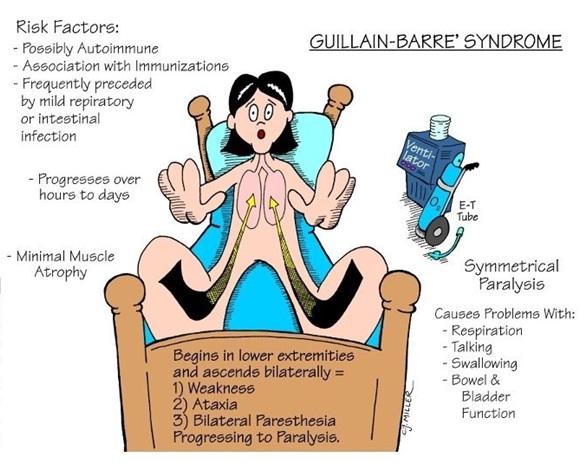
Guillain Barre Syndrome is a rapid-onset muscle weakness as a result of damage to the peripheral nervous system.
It occurs when the body’s immune system attacks part of the nervous system.
Many experience changes in sensation or develop pain, followed by muscle weakness beginning in the feet and hands. The symptoms develop over half a day to two weeks.
It can be divided into the following types:
- Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP)
- Miller Fisher syndrome (MFS)
- Acute motor axonal neuropathy (AMAN)and acute motor-sensory axonal neuropathy (AMSAN)
Causes Of Guillain Barre Syndrome:
The exact cause of Guillain-Barre syndrome is yet unknown.
However, most people develop Guillain-Barre syndrome after having another illness.
This is usually a viral infection, such as the common cold, influenza, a throat infection, or sometimes a bacterial infection
Overall, Guillain-Barre syndrome can be triggered by:
- Most commonly, infection with campylobacter, a type of bacteria often found in undercooked poultry
- Influenza virus
- Epstein-Barr virus
- HIV, the virus that causes AIDS
- Mycoplasma pneumonia
- Surgery
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- Rarely, influenza vaccinations or childhood vaccinations
Symptoms Of Guillain Barre Syndrome:
The following signs and symptoms are exhibited by those suffering from Guillain-Barre syndrome:
- Prickling, “pins and needles” sensations in fingers, toes, ankles or wrists
- Weakness in legs that spreads to the upper body
- Unsteady walking or inability to walk or climb stairs
- Difficulty with eye or facial movements, including speaking, chewing or swallowing
- Severe pain that may feel achy or cramp-like and may be worse at night
- Difficulty with bladder control or bowel function
- Rapid heart rate
- Low or high blood pressure
- Difficulty breathing
- Respiratory failure
- Autonomic dysfunction
Diagnosis Of Guillain Barre Syndrome:
The following procedures help in the diagnosis of Guillain-Barre syndrome:
- Spinal tap (lumbar puncture).
A small amount of fluid is withdrawn from the spinal canal in the lower back. The fluid is tested for a type of change that commonly occurs in people who have Guillain-Barre syndrome.
Thin-needle electrodes are inserted into the muscles the doctor wants to study. The electrodes measure nerve activity in the muscles.
- Nerve conduction studies.
Electrodes are taped to the skin above the nerves. A small shock is passed through the nerve to measure the speed of nerve signals.
Treatment Of Guillain Barre Syndrome:
There are two types of treatment available for Guillain-Barre syndrome.
- Plasma exchange (plasmapheresis).
The liquid portion of part of the blood (plasma) is removed and separated from your blood cells. The blood cells are then put back into the body, which manufactures more plasma to make up for what was removed. Plasmapheresis may work by ridding plasma of certain antibodies that contribute to the immune system’s attack on the peripheral nerves.
- Immunoglobulin therapy.
Immunoglobulin containing healthy antibodies from blood donors is given through a vein (intravenously). High doses of immunoglobulin can block the damaging antibodies that may contribute to Guillain-Barre syndrome.
By : Natural Health News