GHealth A - Z
Gynecomastia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
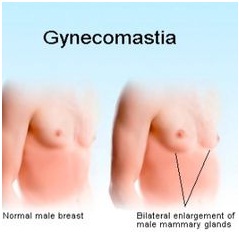
What Is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is a common disorder of the endocrine system in which there is a non-cancerous increase in the size of breast tissue in males.
Gynecomastia can affect one or both breasts, sometimes unevenly.
Causes Of Gynecomastia:
Gynecomastia can occur due to any of the following reasons:
- Natural hormone changes
It can be caused by an altered ratio of estrogens to androgens mediated by an increase in estrogen production, a decrease in androgen production, or a combination of these two factors.
- Side effect of medications
- Anti-androgens
- Anabolic steroids and androgens.
- AIDS medications.
- Anti-anxiety medications, such as diazepam (Valium).
- Tricyclic antidepressants.
- Ulcer medications
- Cancer treatment (chemotherapy).
- Heart medications
- Health conditions
- Hypogonadism
- Aging
- Tumors
- Hyperthyroidism
- Kidney failure
- Liver failure and cirrhosis
- Malnutrition and starvation
- Substance abuse
- Alcohol
- Amphetamines
- Marijuana
- Heroin
- Methadone
Symptoms Of Gynecomastia:
Signs and symptoms may include the following:
- Swollen breast gland tissue
- Breast tenderness
- Pain
- Tenderness
- Nipple discharge in one or both breasts
Diagnosis Of Gynecomastia:
The following procedure is undertaken to diagnose gynecomastia:
- Physical examination
- Blood tests
- Mammograms
- Computerized tomography (CT) scans
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans
- Testicular ultrasounds
- Tissue biopsies
Treatment Of Gynecomastia:
Generally gynecomastia regresses over time without any treatment.
However, if it does not, the following treatment is available:
- Medications
- tamoxifen (Soltamox)
- raloxifene (Evista)
- Surgery
- Liposuction
- Mastectomy
By : Natural Health News




