Hepatopulmonary Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Hepatopulmonary Syndrome?
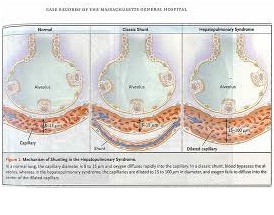
Hepatopulmonary syndrome is a medical condition characterized by shortness of breath and low oxygen level in blood.
It is caused by vasodilation in the lungs. This vasodilation is marked by the widening of arteries, which results from relaxation of smooth muscles within the vessel walls.
It affects people with liver diseases. This includes people affected by fascioliasis, hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, fatty liver disease, and cirrhosis etc. About 20% of patients suffering from liver diseases present with classic signs of Hepatopulmonary syndrome.
Other than liver diseases, the following conditions must be present for the disease to be classified as Hepatopulmonary syndrome:
- Impaired oxygenation
- Intrapulmonary vascular abnormalities, referred to as intrapulmonary vascular dilatations (IPVDs)
To this date, the only known treatment which works against Hepatopulmonary syndrome is liver transplant.
Causes Of Hepatopulmonary Syndrome:
Hepatopulmonary syndrome is caused by pulmonary microvascular vasodilation in patients with portal hypertension (an increase in blood pressure within the system of veins).
The exact mechanism depicting the Hepatopulmonary syndrome is yet unknown. However, it is thought to be related to increase production of hepatic or decreased clearance of hepatic in vasodilators.
The vascular dilation then causes over perfusion relative to ventilation. Increased endogenous nitric oxide (NO) production appears to be the key priming factor for the development of pulmonary vascular dilatation
Vasodilation causes patients to have an increased cardiac output which then results in shortness of breath.
Symptoms Of Hepatopulmonary Syndrome:
The following symptoms are exhibited by those who develop Hepatopulmonary syndrome:
- Symptoms of chronic liver diseases
- Fluid buildup in the belly or abdomen (ascites)
- Vomiting blood, often from bleeding in the blood vessels in the food pipe (esophagus)
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Kidney failure.
- Muscle loss.
- Loss of appetite.
- Dyspnea, which worsen when in upright position
Diangosis Of Hepatopulmonary Syndrome:
Hepatopulmonary syndrome can be diagnosed via:
- Pulse oximetry
- Echocardiography
Treatment Of Hepatopulmonary Syndrome:
Currently, the only known treatment which is effective is liver transplantation. It involves replacing the damaged liver of the patient with some or all of a healthy liver from another person.
With liver transplantation, the 5 year survival rate is 74%, which is comparable to patients who undergo liver transplants who do not suffer from Hepatopulmonary syndrome.
Treatments such as supplemental oxygen or somatostatin used to inhibit vasodilation remain anecdotal and theoretical.
By : Natural Health News




