Hiatal Hernia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
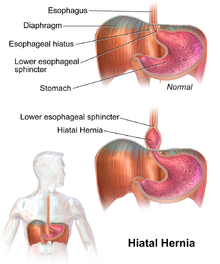
What is Hiatal Hernia?
Hiatal hernia is the protrusion (or herniation) of the upper part of the stomach into the thorax through a tear or weakness in the diaphragm.
Hiatus hernias often result in heartburn but may also cause chest pain or pain with eating.
People with heartburn may experience chest pain that can easily be confused with the pain of a heart attack. That’s why it’s so important to undergo testing and get properly diagnosed.
It is not known how commonly hiatus hernias occur with estimates in North America varying from 10 to 80%.
Causes of Hiatal Hernia:
A hiatal hernia occurs when weakened muscle tissue allows the stomach to bulge up through the diaphragm.
It’s not always clear why this happens, but pressure on the stomach and age-related changes in the diaphragm may contribute to the formation of a hiatal hernia.
Hiatal hernia could be caused by:
- Injury to the area
- Obesity
- Stress
- Being born with an unusually large hiatus
- Persistent and intense pressure on the surrounding muscles, such as:
- when coughing
- vomiting
- straining during a bowel movement
- while lifting heavy objects
Symptoms of Hiatal Hernia:
Generally, small hiatal hernias do not cause any signs and symptoms and are only diagnosed when the doctor sees the bulge while looking for other conditions.
However, larger hiatal hernias can cause signs and symptoms such as:
- Heartburn
- Belching
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chest or abdominal pain
- Feeling especially full after meals
- Vomiting blood or passing black stools, which may indicate gastrointestinal bleeding
- Shortness of breath
- Heart palpitations
Diagnosis of Hiatal Hernia:
A hiatal hernia is often discovered during a test or procedure to determine the cause of heartburn or chest or upper abdominal pain.
Such tests or procedures include:
- Blood testing.
- A complete blood count to check for anemia due to blood loss.
- An esophagram (barium swallow).
- Endoscopy, to check for inflammation
- Manometry, to measure pressure and movement inside the esophagus.
Treatment of Hiatal Hernia:
In case of small hiatal hernia, one doesn’t experience any symptoms and therefore doesn’t require any treatment.
However, if signs and symptoms are exhibited, the following treatment options are available:
- Medications for heart burn
- Antacids that neutralize stomach acid
- Gelusil
- Maalox
- Mylanta
- Rolaids
- Tums
- Medications to reduce acid production.
- cimetidine (Tagamet HB)
- Famotidine (Pepcid AC)
- nizatidine (Axid AR)
- Ranitidine (Zantac 75)
- medications that block acid production and heal the esophagus
- lansoprazole (Prevacid 24HR)
- omeprazole (Prilosec OTC)
- Surgery to repair hernia
- Nissen fundoplication
By : Natural Health News