Hip Labral Tear Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
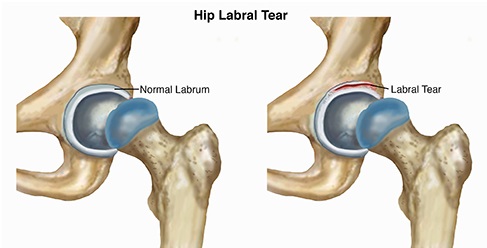
What Is Hip Labral Tear?
Also known as acetabular labral tear, hip labral tear is damage to the cartilage and tissue in the hip socket.
The affected acetabular labrum generally provides an articulating surface for the acetabulum, allowing the head of the femur to articulate with the pelvis. It is also necessary for maintain the stability of the joint.
Hip labral tear may or may not cause exhibition of symptoms. In some cases it may cause development of pain in the groin.
A labral tear results when a part of the labrum separates or is pulled away from the socket. Possible causes range from direct trauma to indulging in sports that require repetitive motion of the hips. Moreover, structural abnormalities may also play a role in development of hip labral tear.
If not treated, hip labral tears may lead to permanent damage to the joint, and therefore treatment should not be avoided.
Causes Of Hip Labral Tear:
Hip labral tear may result from a number of factors. This may include:
- Bony abnormalities in the hip joint (hip impingement)
- Hip muscle tightness
- Hip muscle weakness
- Improper technique with repetitive activities
- Participation in sports that require distance running, or repetitive twisting and cutting
Symptoms Of Hip Labral Tear:
The following symptoms may be exhibited by those who suffer from hip labral tear:
- A locking, clicking or catching sensation in hip joint
- Pain in hip or groin
- Stiffness or limited range of motion in hip joint
- Pain experienced when swatting or exercising
- Osteoarthritis may develop as a complication
Diagnoses Of Hip Labral Tear:
Hip labral tear may be diagnosed via:
- Imaging tests
- X-rays to visualize the affected bone
- MRI, to detect structural abnormalities
- Anesthesia injection
- If it relieves pain, it showcases that the problem is inside the hip joint
Treatment Of Hip Labral Tears:
Treatment depends on the severity of hip labral tears. The following treatment options are available:
- Medications, to relieve pain and reduce inflammation
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others)
- naproxen (Aleve)
- Therapy
- exercises to maximize hip range of motion and hip strength and stability
- Surgery
- arthroscopic surgery
By : Natural Health News




