Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
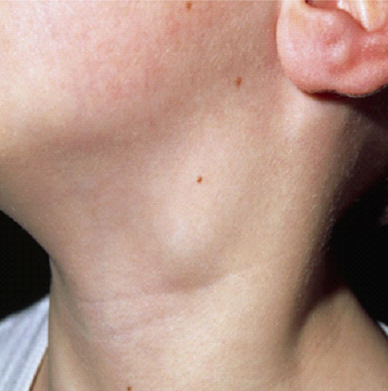
What is Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
Lymph tissue dwells in the lymphatic system and precisely in the lymph nodes, liver, spleen, bone marrow and in some other parts. Lymphatic system contains cells that are responsible to eliminate any infectious and bacterial objects from the body. When these cells grow abnormally and surpass the lymphatic system, the ability of the system of fight infectious particles decline. Fortunately due to medical advancements, complete recovery from Hodgkin’s disease is possible. Researches and case studies suggest that non-hodgkin’s disease, which is one of the two forms of lymphatic system cancers, is more common.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
During Hodgkin’s lymphoma, the following symptoms may evolve:
- Deteriorating appetite.
- Constant weariness.
- Itch.
- Fever.
- Chills.
- Sweating at night.
- Aching lymph nodes after drinking alcohol.
- Weight loss.
While these are some of the most common symptoms evolving in Hodgkin’s lymphoma, skin blushing, coughing and breathing problems may also show up.
How Is Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Caused?
Hodgkin’s lymphoma has several types. A different category of cells are involved in each type. A mutation in the DNA assists these cells to grow abnormally and survive while ruling out healthy cells. Due to this process, symptoms of Hodgkin’s lymphoma start to evolve.
- Classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma is a common type of this disease. The cells involved in classical Hodgkin’s disease are known as reed-Sternberg cells. Lymphocyte-depleted Hodgkin’s lymphoma and nodular sclerosis Hodgkin’s lymphoma are the subtypes of Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
- A rarely found type is known as lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin’s lymphoma in which the cells involved are known as popcorn cells primarily due to their shape.
What Are The Risk Factors Of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
The following factors increase the risk of Hodgkin’s lymphoma:
- A compromised immune system.
- Males.
- Family history i.e. a family member having or used to have Hodgkin’s or non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
- Ages of between 15 and 30 years and older than 55 years.
- Medical history involving illnesses caused due to Epstein-Barr infection.
How Is Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Diagnosed?
Certain tests are helpful in diagnosing Hodgkin’s lymphoma:
- Removal of a swollen lymph nodes surgery.
- Testing bone marrow.
- Blood tests.
- X-ray.
- Computerized tomography or CT scan and positron emission tomography or PET.
- Physical exam involving neck, groin and underarm.
Doctors do not only need to diagnose Hodgkin’s lymphoma but also determine its stage. Stages start from 1 and ends on 1V depending on the severity of the condition. Also, the letter A indicates that no prominent symptoms evolve due to cancer and letter B indicates that significant symptoms do evolve.
How Is Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Treated?
The treatment of Hodgkin’s lymphoma depends on the stage and type of disease. Whatever treatment method is used, the aim is to eliminate cancer cells to the maximum and for disease remission. The following procedures are commonly used:
- Radiation.
- Chemotherapy.
- Transplantation of stem cells.
Massage, acupuncture, medications, aromatherapy and meditation are some alternative ways of treating the symptoms of Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Staying active and getting enough rest could help the victims lead a better life during Hodgkin’s disease.
By : Natural Health News




