Liver Hemangioma Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
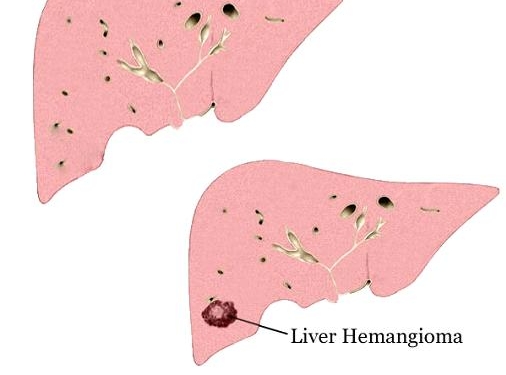
What Is Liver Hemangioma?
It is a noncancerous tumor (mass) which forms in the liver. Furthermore, tangled blood vessels are responsible for creating this benign mass, called liver hemangioma. Usually, liver hemagiomas are revealed in certain procedures or tests conducted for some other medical condition. Majority individuals with liver hemangioma do not feel any symptoms at all, thus do not require treatment.
Of course, being aware of a mass in the liver can be very disturbing, even though it is non cancerous. No evidence proves that liver hemangioma can proceed to liver cancer, if left untreated.
What Are The Alternate Names Of Liver Hemangioma?
Liver hemangioma is also known by the following names:
- Hemangioma of the liver.
- Multinodular hepatic hemangiomatosis.
- Infantile hemangioendothelioma.
- Cavernous hepatic hemangioma.
What Are The Symptoms Of Liver Hemangioma?
In majority instances of liver hemangiona, it never advances (grows) and sources any symptoms. However in small proportion of instances, it advances and cause complications. Indeed, treatment then becomes mandatory. Why liver hemangioma grows in few cases leading complications and why not in others, is unknown till date. Few symptoms may include:
- Interference with normal functioning of liver.
- Bleeding.
- Hemangioma can rupture (in rare instances).
What Causes Liver Hemangioma?
The exact cause that roots the formation of liver hemangioma is ambiguous. However; according to the doctors, it is congenital, which means that hepatic hemangioma can be a birth defect. It is among the common forms of liver tumor. It can occur at any age; however it is more common in individual between the ages of thirties-fifties. As compared to males, females develop liver hemangioma more often, with a bigger tumor.
Even babies can experience a form of hepatic hemangioma known as benign infantile hemangioendothelioma. The form is a rare, benign tumor associated with high rates of death and heart failure in babies. Often, infants are diagnosed with benign infantile hemangioendothelioma by the time they reach five to six months of age.
What Are The Possible Complications Of Liver Hemangioma?
Estrogen-based medications and pregnancy can make the tumors grow larger. This will lead to the emergence of symptoms, ultimately needing treatment!
How Is Hemangioma Diagnosed?
Usually, liver hemagiomas are revealed in certain procedures or tests conducted for some other medical condition. However following can help diagnose a liver hemangioma:
- MRI.
- CT scan.
- Ultrasound.
- Single-photon emission CT scan.
The doctor can recommend few other procedures and tests depending upon the situation.
How Is Liver Hemangioma Treated?
Majority individuals with liver hemangioma do not feel any symptoms at all, thus do not require treatment. Treatment is needed if there is constant pain. Its treatment relies on the situation, for example:
- Size and location of hemagioma.
- Patient’s preferences.
- Overall health.
- Weather the patient has a single or more hemagioma.
Few treatment options of liver hemangioma are:
- Radiation therapy.
- Liver transplant surgery.
- Procedures such as arterial embolization and hepatic artery ligation to stop blood flow to your hemangioma.
- Surgery to eliminate liver hemangioma.
Related Articles:
Enlarged Liver Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Amebic Liver Abscess Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Alcoholic Liver Disease Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Acute Liver Failure Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Tylenol Liver Damage Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Fatty Liver Diet plan and how does it works?
Fatty Liver Disease Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Liver Hemangioma Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
By : Natural Health News




