Menorrhagia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Menorrhagia ?
A type of abnormal uterine bleeding, menorrhagia is a type of menstrual period which is characterized by abnormality in quantity, timing, or duration of bleeding.
Periods are considered heavy if there is enough bleeding to soak a pad or tampon every hour for several consecutive hours. Such heavy periods may interfere with sleep and other daily activities.
Treatment of menorrhagia varies according to the severity, cause, and level of disruption caused in daily functioning. Possible treatments range from prescribing contraceptive pills to surgery.
Having heavy bleeding during menstrual periods is relatively common. However, not all of such cases are dubbed to be menorrhagia. Approximately 53 in 1000 women are diagnosed by menorrhagia or other types of abnormal uterine bleeding.
Other types of abnormal uterine bleeding include polymenorrhea, oligomenorrhea, metrorrhagia and postmenopausal bleeding.
Causes Of Menorrhagia:
A variety of causes can bring about menorrhagia. They may include:
- Hormonal imbalance
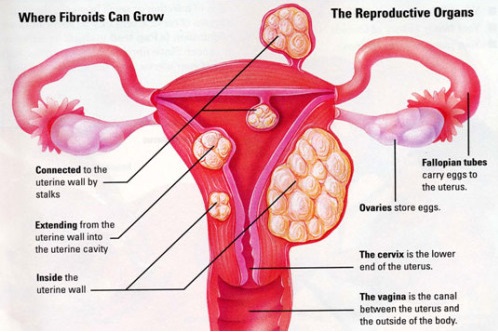
- Fibroids or noncancerous tumors of the uterus
- Miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy
- Use of blood thinners
- Problems with a non-hormonal intrauterine device used for birth control
- Adenomyosis
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Uterine, ovarian cancer, and cervical cancer
- Other medical conditions that can prevent normal blood clotting
- Liver disease
- kidney disease
- thyroid disease
- bleeding disorders
- platelet disorders
- Dysfunction of ovaries
- Polyps
- Infections or tumors in the pelvic cavity
- High levels of prostaglandins (chemical substances which help to control the muscle contractions of the uterus)
- High levels of Endothelin (chemical substances which help the blood vessels in the body dilate)
Menorrhagia is likely to affect either young girls who just started menstruating or older women who are approaching menopause.
Symptoms Of Menorrhagia:
The following signs and symptoms may be exhibited:
- Nighttime bleeding that requires getting up to change pads or tampons
- Passing large blood clots during menstruation
- A period that lasts longer than seven days
- Fatigue
- Anemia
- Shortness of breath
- The need to change pads or tampons every hour
- Needing to use double sanitary protection
- Restricting daily activities due to heavy menstrual flow
Diagnosis Of Menorrhagia:
Menorrhagia can be diagnosed via:
- Physical examination, which includes pelvic exam
- Medical history
- Blood tests
- Pap test, to detect changes that may be cancerous or may lead to cancer, and to show noncancerous conditions, such as an infection or inflammation.
- Ultrasound
- Biopsy (endometrial)
- Dilation and curettage (D & C).
Treatment Of Menorrhagia:
Treatment depends on the severity and cause of menorrhagia. The following treatment options are available:
- Iron supplementation.
- Used if menorrhagia is accompanied by anemia
- Prostaglandin inhibitors, to reduce cramping and blood loss
- Aspirin
- ibuprofen
- Oral contraceptives, to inhibit ovulation.
- Progesterone Hormone treatment.
- Endometrial ablation, to destroy the lining of the uterus (endometrium).
- Endometrial resection, to remove the lining of the uterus (endometrium).
- Hysterectomy
- Uterine artery embolization.
By : Natural Health News