Myocardial Ischemia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Myocardial Ischemia?
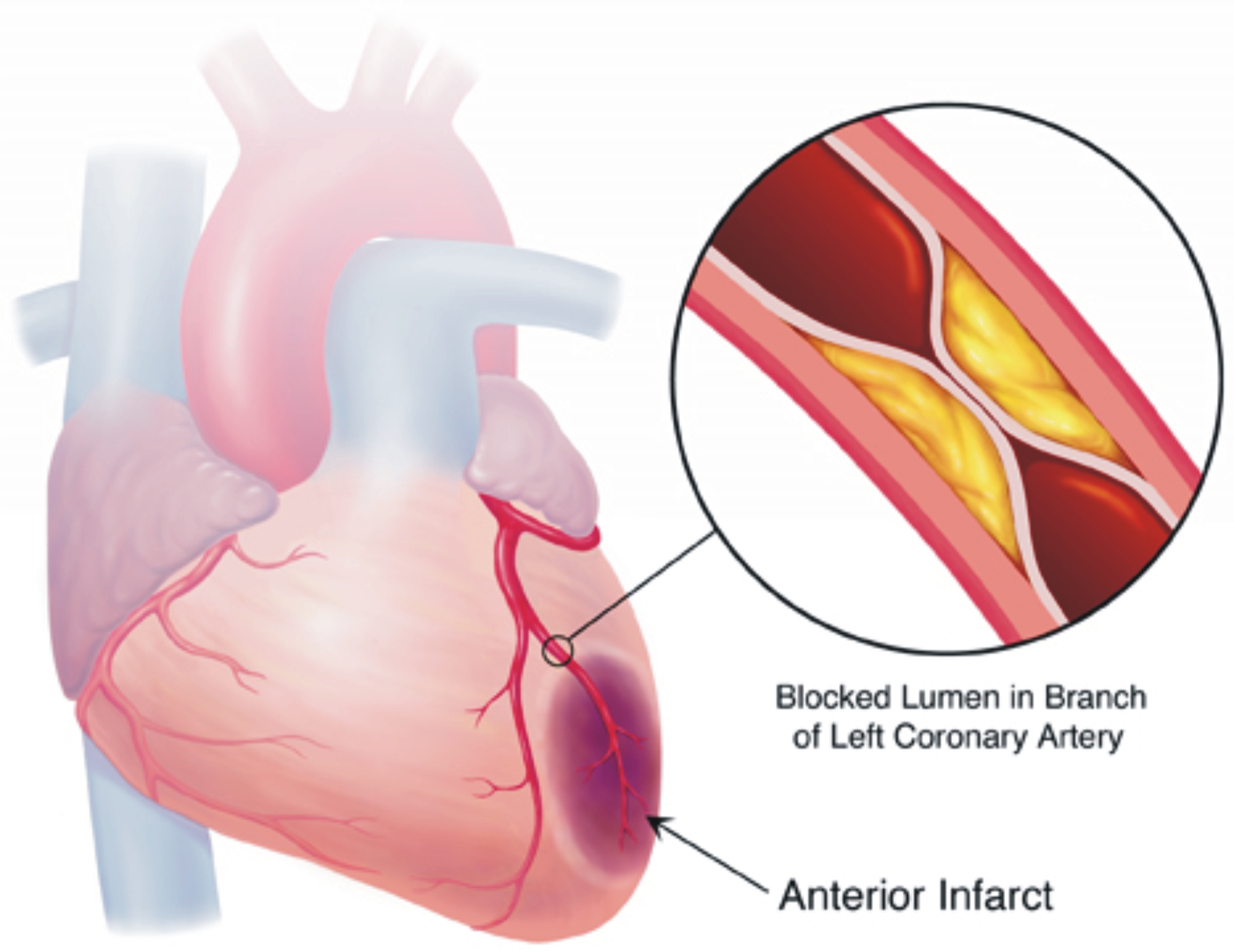
Myocardial ischemia is a disorder that usually is caused by a critical coronary artery obstruction, which is also known as atherosclerotic coronary artery disease (CAD).
Myocardial ischemia occurs when blood flow to the heart is reduced, preventing it from receiving enough oxygen. The reduced blood flow is usually the result of a partial or complete blockage of the heart’s arteries (coronary arteries).
Myocardial ischemia, also called cardiac ischemia, can cause damages to the heart muscle, reducing its ability to pump efficiently.
A sudden, severe blockage of a coronary artery can lead to a heart attack. It might also cause serious abnormal heart rhythms.
Treatment for myocardial ischemia involves improving blood flow to the heart muscle. It may include medications, a procedure to open blocked arteries or bypass surgery.
Myocardial ischemia is known to result in serious complications, including:
- Heart attack.
If a coronary artery becomes completely blocked, the lack of blood and oxygen can lead to a heart attack that destroys part of the heart muscle. - Irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia).
An abnormal heart rhythm can weaken the heart and may be life-threatening. - Heart failure.
Myocardial ischemia can damage the heart muscle, reducing its ability to effectively pump blood to the rest of the body.
Causes Of Myocardial Ischemia:
Myocardial ischemia occurs when the blood flow through one or more of the coronary arteries decreases.
Possible conditions that may cause myocardial ischemia may include:
- Coronary artery disease (atherosclerosis).
Plaques made up mostly of cholesterol build up on the artery walls and restrict blood flow. - Blood clot.
The plaques that develop in atherosclerosis can rupture, causing a blood clot. The clot might block an artery and lead to sudden, severe myocardial ischemia, resulting in a heart attack. - Coronary artery spasm.
This temporary tightening of the muscles in the artery wall can briefly decrease or even prevent blood flow to part of the heart muscle.
Myocardial Ischemia is most commonly experienced during:
- Exercise or exertion
- Eating
- Excitement or stress
- Exposure to cold
The Following Factors Increase The Risk Of Developing Myocardial Ischemia:
- Tobacco
- Diabetes.
- High blood pressure
- High blood cholesterol level
- High blood triglyceride level
- Obesity
- Waist circumference
- Lack of physical activity
Symptoms Of Myocardial Ischemia:
Some people who have ischemia don’t experience any signs or symptoms.
When signs and symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Neck or jaw pain
- Shoulder or arm pain
- A fast heartbeat
- Shortness of breath when you are physically active
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sweating
- Fatigue
- Chest pain
Diagnosis Of Myocardial Ischemia:
The following diagnostic tests are conducted in order to confirm the diagnosis:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Echocardiogram, which helps identify whether an area of the heart has been damaged and isn’t pumping normally.
- Nuclear scan, allows blood-flow problems to be identified
- Coronary angiography
- Cardiac CT scan
- Stress test
Treatment Of Myocardial Ischemia:
Treatment options include:
- Medications
Aspirin.
Nitrates.
Beta blockers.
Calcium channel blockers.
Cholesterol-lowering medications.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors.
Ranolazine (Ranexa). - Procedures to improve blood flow
Angioplasty and stenting
Coronary artery bypass surgery
Enhanced external counter pulsation.
By : Natural Health News




