Osteoporosis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What is Osteoporosis:
Osteoporosis is a sickness in which bones get to be delicate and more inclined to break. Normally the bone loses thickness, which measures the measure of calcium and minerals in the bone. Osteoporosis is the most well-known sort of bone malady.
In light of osteoporosis about 50% of all ladies beyond 50 years old will have a break of the hip, wrist, or vertebra amid their lifetime.
Bone is existing tissue. Existing bone is continually being supplanted by new bone. Osteoporosis happens when the body neglects to structure enough new bone, when an excess of existing bone is reabsorbed by the body, or both.
Calcium is one of the imperative minerals required for bones to structure. On the off chance that you don’t get enough calcium and vitamin D, or your body does not ingest enough calcium from your eating regimen, your bones may get to be weak and more inclined to crack.
Off and on again bone misfortune happens without any reason. Caucasian ladies are more prone to have bone misfortune. Some of the time the inclination to have bone misfortune and slight bones is passed down through families.
Causes of Osteoporosis:
A drop in estrogen in ladies at the time of menopause and a drop in testosterone in men is a main reason for bone misfortune. Different reasons for bone misfortune include:
- Certain restorative conditions
- Taking certain drugs
- Nonappearance of menstrual periods for drawn out stretches of time
- A family history of osteoporosis
- Drinking a lot of liquor
- Low body weight
Symptoms of Osteoporosis:
Osteoporosis itself has no symptoms. It only has dire consequences in the form of fractures and broken bones.
It is generally characterized by:
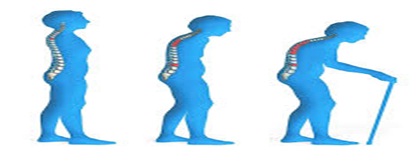
- Back pain, caused by either a fracture or a collapsed vertebra
- A stooped posture
- Loss of height
- Bone fracture
- Debilitating acute and chronic pain
- Increase risk of falling
Diagnosis of Osteoporosis:
Osteoporosis can be diagnosed by the following methods:
- Conventional radiography
This is useful in detecting complications of osteoporosis. Complications may include:
- reduced bone mass
- preosteoporosis such as fractures
- Dual energy X-ray
Osteoporosis is diagnosed when the bone mineral density is less than or equal to 2.5 standard deviations below that of a young (30–40-year-old), healthy adult women reference population. This is translated as a T-score. The T-score is then compared to the guideline provided by the World Health Organization in order to diagnose osteoporosis.
- Biomarkers which help in detecting bone degradation
Treatment of Osteoporosis:
Handling osteoporosis may include:
- Way of life changes, for example, eating methodology and activity
- Taking calcium and vitamin D
- Utilizing medications
A bone break has happened and a bone thickness test demonstrates that you have meager bones, however not osteoporosis.
Solutions used to treat osteoporosis include:
- Bisphosphonates
- Estrogens, calcitonin,raloxifene, teriparatide,
- Activity assumes a key part in saving bone thickness in more seasoned grown-ups. A percentage of the activities prescribed to decrease your shot of a break include:
- Weight-bearing activities
- Free weights, weight machines, stretch groups
- Parity works out
- Paddling machines
Evade any practice that introduces a danger of falling. Additionally, don’t do high-effect practices that can result in cracks in more established grown-ups.
By : Natural Health News