Patent Ductus Arteriosus PDA Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
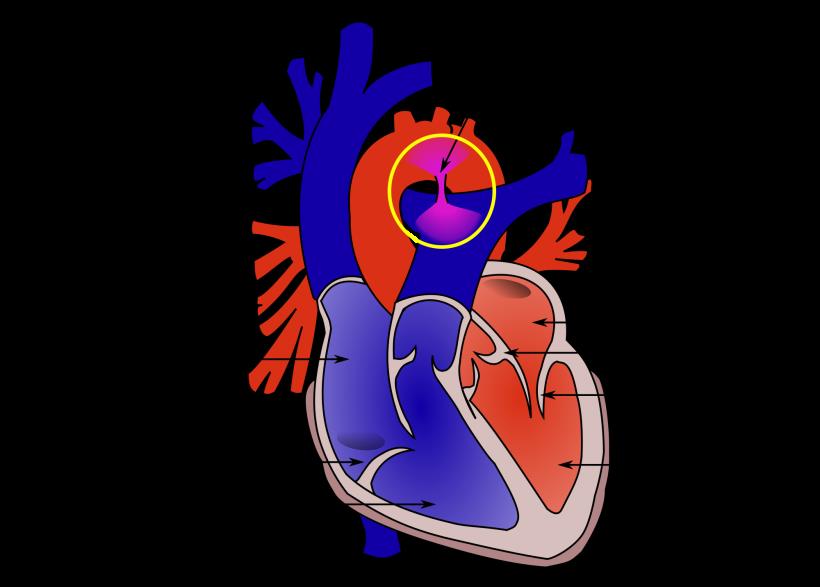
What Is Patent Ductus Arteriosus PDA?
Patent ductus arteriosus PDA is a congenital heart defect wherein the ductus arteriosus fails to close after birth.
This persistent opening between two major blood vessels leading from the heart, ductus arteriosus is a normal part of a baby’s circulatory system before birth that usually closes shortly after birth.
However, if it doesn’t, it is termed as a heart defect.
Causes Of Patent Ductus Arteriosus PDA:
There is no clear cause for PDA. However, it is speculated that environment and genetics may play a role.
The following factors increase the likelihood of developing PDA:
- Premature birth.
- Family history and other genetic conditions.
- Rubella infection during pregnancy
- Being born at a high altitude
Symptoms Of Patent Ductus Arteriosus PDA:
Some common symptoms of PDA include the following:
- tachycardia (a heart rate exceeding the normal resting rate)
- respiratory problems
- dyspnea (shortness of breath)
- continuous machine-like heart murmur
- cardiomegaly (enlarged heart, reflecting ventricular dilation and volume overload)
- left subclavicular thrill
- bounding pulse
- widened pulse pressure
- poor growth
- Differential cyanosis, i.e. cyanosis of the lower extremities but not of the upper body.
Diagnosis Of Patent Ductus Arteriosus PDA:
The following tests are conducted to diagnose PDA:
- Echocardiogram
- Chest X-ray
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Cardiac catheterization
Treatment Of Patent Ductus Arteriosus PDA:
PDA can be treated via the following procedures:
- Medications
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- ibuprofen
- indomethacin
- Preventive antibiotics
- Open heart surgery
- Catheter procedures
By : Natural Health News




