Pilonidal Cyst Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
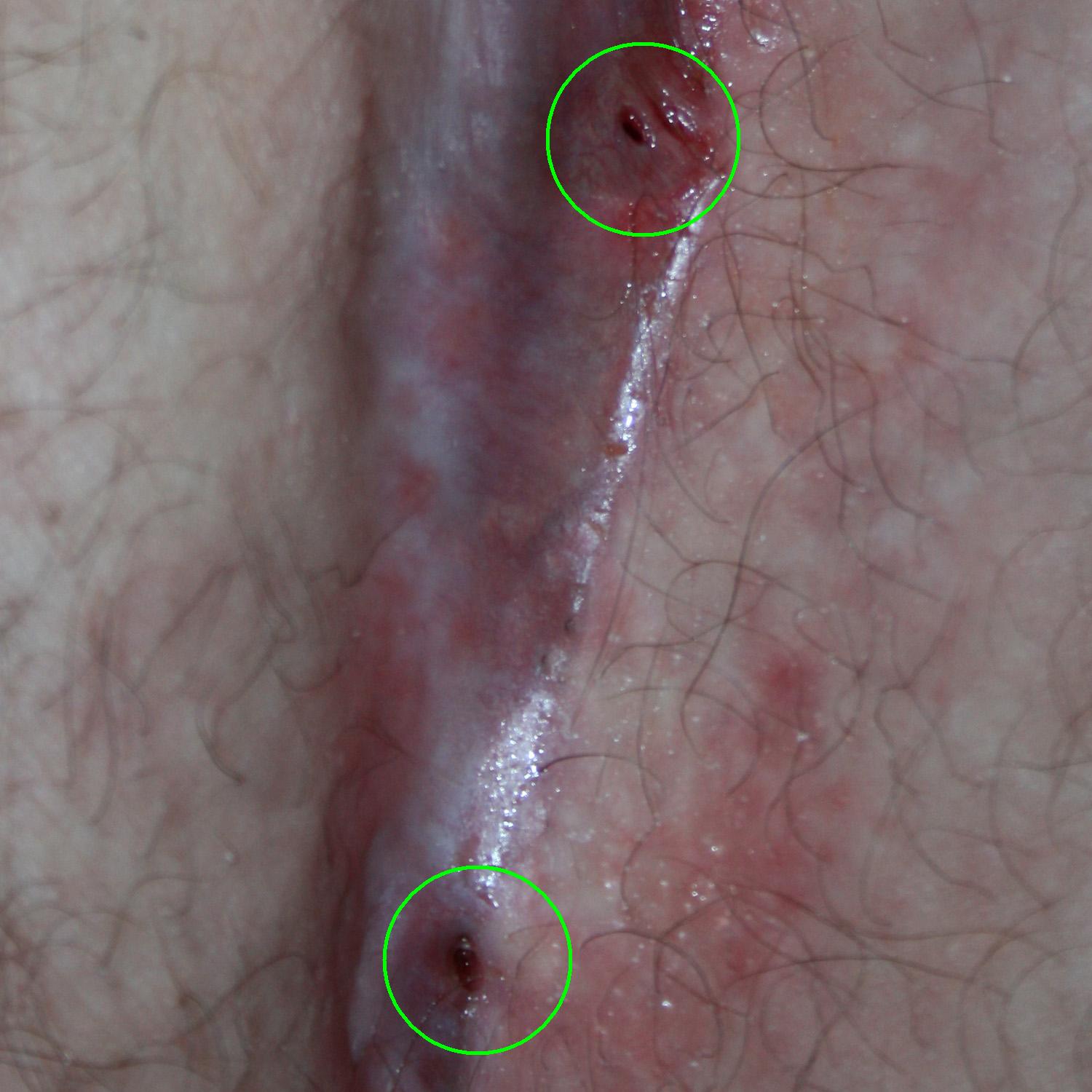
What Is Pilonidal Cyst?
Pilonidal cysts are abnormal hole in the skin. It usually occurs at the cleft of the buttocks and the tailbone. The skin in question, usually contains hair and skin debris.
Pilonidal cysts generally occur when the hair ruptures the skin and becomes embedded. If such cysts become infected, a painful abscess will be formed.
People who are involved in sedentary work, such as office workers, are more likely to develop pilonidal cyst.
Pilonidal cysts can be treated via draining it through a small incision or removed surgically.
If not treated promptly and effectively, pilonidal cysts can develop into a type of skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma.
Causes Of Pilonidal Cyst:
The exact cause of pilonidal cyst is yet unknown. However, a few theories have been proposed.
Most doctors reckon that ingrown hairs are a core cause of pilonidal cysts. This is due to the fact that hair follicles are found inside the cyst.
Another possible theory is that pilonidal cysts may appear after trauma to that region of the body. This is due to the observation that during world war two, more than 50000 soldiers developed pilonidal cysts.
Possible risk factors may include:
- Male sex
- Younger age
- Obesity
- Inactive lifestyle
- Occupation requiring prolonged sitting
- Excess body hair
- Stiff or coarse hair
Symptoms Of Pilonidal Cyst:
Often very painful, pilonidal cysts typically affect people between the ages of 15 and 35.
Possible symptoms include:
- Pain/discomfort or swelling above the anus or near the tailbone that comes and goes
- Opaque yellow (purulent) or bloody discharge from the tailbone area
- Unexpected moisture in the tailbone region
- Discomfort with sitting on the tailbone, doing sit-ups or riding a bike (any activities that roll over the tailbone area)
- Fever
- Reddening of the skin
Diagnosis Of Pilonidal Cyst:
Pilonidal cyst can be diagnosed via:
- Medical history
- Physical examination
The following conditions may be detected during the physical exam:
- Tenderness, redness, and swelling between the cheeks of the buttocks just above the anus
- Increased white blood cells on a blood sample
- Inflammation of the surrounding skin
Treatment Of Pilonidal Cyst:
If the pilonidal cyst is not infected, no treatment is required.
If infected, surgery is required. In a relatively minor operation, incision and drainage, involving the opening of sinus and draining away the pus, is done.
- After surgery, the surgeon may choose to:
Leave the wound open.
This results in a longer healing time but lowers the risk of a recurring pilonidal cyst infection. - Close the wound with stitches.
This is marked by a shorter healing time but with a higher risk of recurrence.
Related Articles:
Bursitis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Folliculitis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Carcinoid Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Buerger’s Disease Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Shingles Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Chilblains Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Cradle Cap Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Contact Dermatitis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Cold Urticaria Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Henoch Schonlein Purpura (HSP) Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Soft Tissue Sarcoma Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
By : Natural Health News




