Raynaud’s Disease Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
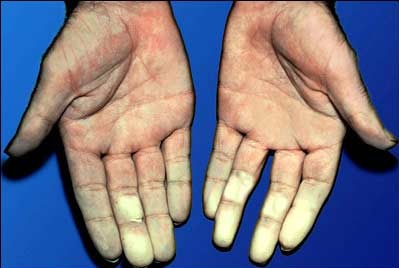
What Is Raynaud’s Disease ?
Also known as Raynaud’s phenomenon, Raynaud’s disease is an uncommon disorder which is marked by excessive reduction in blood flow in response to either cold temperature or extreme stress.
Affected location may include fingers and toes. In Raynaud’s disease, smaller arteries responsible for supplying blood to the skin may narrow which causes a hindrance in blood flow. This process is also referred to as vasospasm.
Women are more prone to developing Raynaud’s disease than men. Moreover, living in a cold climate greatly increases the risk of developing it.
While developing Raynaud’s disease greatly affects quality of life, it may not prove to be disabling if treatment is sought.
There are two types of Raynaud’s disease namely:
- primary – when the condition is idiopathic in nature
- secondary – when another medical condition is the underlying cause
Causes Of Raynaud’s Disease:
When Raynaud’s disease is primary in nature, it is not caused by any other condition and is idiopathic in nature.
If it is secondary in nature, possible causes include:
- Connective tissue diseases.
- Diseases of the arteries.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Repetitive action or vibration.
- Smoking
- Certain medications.
Possible risk factors include:
- Women are at a higher risk of developing it than men
- Primary Raynaud’s begins between the ages of 15 and 30.
- Living in a colder climate increases the risk of developing the condition
- Family history.
- Having a first degree relative greatly increases the risk of developing the disease
Symptoms Of Raynaud’s Disease:
Signs and symptoms may vary in severity and location, and may include the following:
- Cold fingers or toes
- Color changes in skin in response to cold or stress
- Numb, prickly feeling or stinging pain upon warming or stress relief
Diagnosis Of Raynaud’s Disease:
Raynaud’s disease can be diagnosed via:
- Antinuclear antibodies test, whose positive result may indicate a stimulated immune system
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, ,which indicates presence of an autoimmune disease
Treatment Of Raynaud’s Disease:
The following treatment options are available:
- Medications
- Calcium channel blockers.
- Afeditab CR
- Procardia
- mlodipine (Norvasc)
- felodipine (Plendil
- Alpha blockers.
- prazosin (Minipress)
- doxazosin (Cardura).
- Surgery
- Nerve surgery
- Chemical injection
Related Articles:
Swimmers Itch Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Tularemia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and treatment
Cold Sores Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Hemangioma Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Progeria Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Stye Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Castleman Disease Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Diaper Rash Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Cellulitis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Tinea Versicolor Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Prickly Heat Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
By : Natural Health News




