Rickets Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
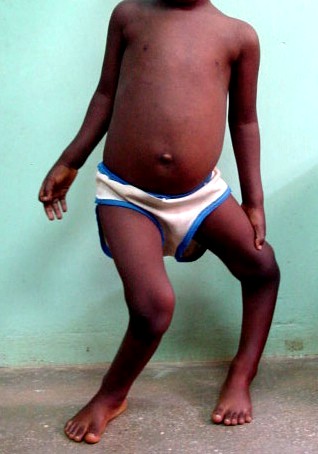
What Are Rickets?
It is a disorder that makes a child’s bones weak and soft. It is triggered by prolonged deficiency of phosphate, calcium and vitamins D in the body.
What Are The Symptoms Of Rickets?
Few common symptoms of rickets are:
- Bone tenderness or pain:
1. Spine.
2. Pelvis.
3. Legs.
4. Arms.
- Dental deformities.
- Impaired growth.
- Skeletal deformities.
- Short stature.
- Muscle cramps.
- Increased bone fractures.
What Causes Rickets?
Clearly, consuming a diet that lacks sufficient levels of phosphate and calcium makes you more prone to contract rickets. Our body needs sufficient vitamin D to control the levels of phosphate and calcium. In case the blood levels of these essential mineral drops considerably low, it results in the making of hormones that cause phosphate and calcium to release from your bones. Such tends to consequent in soft and weak bones.
There are two sources of vitamin D:
- From the food we eat: deficiency of vitamin D occurs when you do not consume dairy products, are lactose intolerance or vegetarian.
- Made by our skin when being exposed to sun: Deficiency occurs when you stay indoor mostly, have little to no sun exposure.
Moreover, a form of rickets, known as hereditary rickets, is transmitted from families.
What Are The Risk Factors Of Rickets?
A number of factors that raises the chances of a child to develop rickets are:
- Children with darker skin color are more likely to develop rickets as dark skin makes less vitamin D as compared to lighter skin.
- Breast feeding babies as breast milk lacks sufficient levels of vitamin D needed to prevent the disorder.
- Children who are less exposed to sun due to climatic conditions or who stays indoor most of the time.
- Taking anti-seizure drugs.
- Children between three months to three years old.
- Premature birth.
How Is Rickets Diagnosed?
During the visit, the doctor will carry out a thorough physical exam. The exam will reveal pain or tenderness in the patient’s bone. Following tests can be useful in diagnosing rickets:
- Serum phosphorus.
- Serum alkaline phosphate.
- Bone X-rays.
- Bone biopsy.
- Blood tests.
- Arterial blood gases.
Some other procedures and tests that can also be recommended include:
- Urine calcium.
- PTH.
- Calcium (ionized).
- ALP isoenzyme.
How Are Rickets Treated?
The treatment of rickets aims to ease the symptoms and fix the cause that has lead to the disorder. Its treatment mainly involves around restoring the levels of vitamin D, phosphorus or calcium. This can help the symptoms to resolve considerably.
Moreover, the patient is emphasized to intake vitamin D through dietary sources that is processed milk, liver, fish etc. Besides, moderate level of sunlight exposure is also important.
In case the disease is sourced by a metabolic problem, then the doctor can recommend supplements of vitamin D to the patient. In order to avert or lessen deformities, bracing or positioning can be used. Few instances of skeletal deformities can need corrective surgery.
By : Natural Health News




