Sclerosing Cholangitis Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
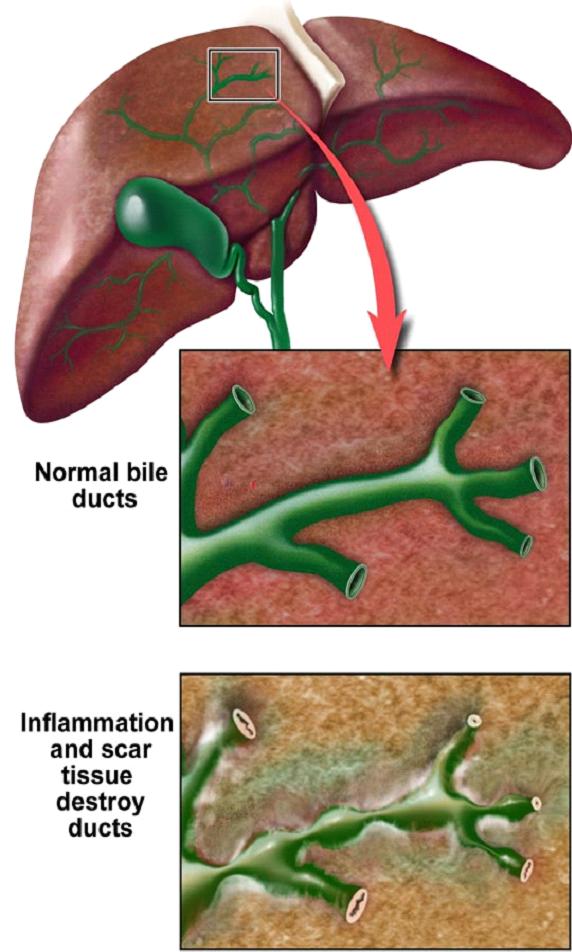
What Is Sclerosing Cholangitis?
Our liver releases bile. It is a liquid that contains waste products, bile salts and cholesterol. Bile salts are needed by our body to digest fats. The liver releases out the bile through our bile ducts. It is then stored in our gallbladder where it is released into our small intestine after consuming a meal.
Sclerosing cholangitis is the disease of bile ducts. In the disease, inflammation tends to trigger scars within your bile ducts. Furthermore, these scars cause the ducts to become narrow and hard, slowly leading to an acute liver damage.
Usually, the disease gradually advances and leads to tumors of the liver or bile duct, repeated infections, and even liver failure! The mere cure for sclerosing cholangitis is liver transplant. However its treatment involves easing your symptoms and screening your liver functions. At times, doctors perform specific procedures that unblock the blocked ducts to provide temporary relief.
What Are The Symptoms Of Sclerosing Cholangitis?
Often, initial symptoms are yellowing of the eyes and skin, itching and fatigue whereas few individuals can have no signs at all.
Some other symptoms tend to include:
- Enlarged spleen and liver.
- Weight loss.
- Loss of appetite.
- Recurrent episodes of cholangitis.
What Causes Sclerosing Chalngitis?
Doctors believe genetic factors to play a vital role in its instigation. Besides it can also be sourced by the following:
- Infections in the bile ducts, gallbladder and liver.
- Choledocholithiasis.
Moreover; it is observed in people who have the following:
- Sarcoidosis.
- Inflammatory bowel disease for example ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
- Chronic pancreatitis.
- Autoimmune disorders.
What Are The Risk Factors Of Sclerosing Cholangitis?
The disorder is rarely diagnosed in children; however it is more common in males as compared to females.
What Are The Potential Complications Of Sclerosing Cholangitis?
Sclerosing cholangitis can lead to a number of serious complications if not treated promptly.
Few of such complications include:
- Vitamin deficiencies.
- Bleeding esophageal varices.
- Cholangiocarcinoma (cancer that develops in the bile ducts).
- Liver failure.
- Cirrhosis.
- Strictures- narrowing of bile ducts.
- Cholangitis- infection of biliary system.
How Is Sclerosing Cholangitis Diagnosed?
Following tests can help diagnose sclerosing cholangitis:
- Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram.
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.
- Liver biopsy.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
- Abdominal ultrasound.
- Abdominal CT scan.
- Blood tests (liver function tests).
How Is Sclerosing Cholangitis Treated?
As mentioned earlier, its treatment involves easing your symptoms and screening your liver functions. Following medications are often prescribed to the patients of sclerosing cholangitis:
- Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K).
- Cholestyramine.
- Medications that helps to quite the overactive immune system such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, azathioprine, prednisone.
- Antibiotics for treating the bile duct infections.
- Ursodeoxycholic acid.
Surgical procedures include:
- Liver transplant.
- Protocolectomy.
- Inserting a tube or drain for narrow biliary ducts.
- Endoscopic balloon dilation of narrow ducts.
What Is The Prognosis Of Sclerosing Cholangitis?
How well people with sclerosing scholangitis do, depends. Often, the disease worsens gradually whilst at times, patients experience life-threatening complications lead by sclerosing cholangitis.
By : Natural Health News




