Secondary Hypertension Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Secondary Hypertension ?
Secondary hypertension, also known as inessential hypertension, is a form of hypertension which is caused by an underlying identifiable secondary cause.
It tends to develop in approximately 5% of the total hypertension patients. They are known to result from conditions which affect various organs ranging from kidneys, arteries, heart to the entire endocrine system.
It also has a tendency to occur during pregnancy and can prove to be dangerous for the fetus as well as the expectant mother.
While primary hypertension, including high and low blood pressure, does not have a known cause, secondary hypertension does. And this may lead to a better treatment and hence better managing chances of the disease.
Secondary hypertension may lead to development of a series of complications which may include high blood pressure, kidney failure and stroke. These complications can be avoided via effective treatment.
Causes Of Secondary Hypertension:
Secondary hypertension can arise either as a side effect to certain medications or due to medical conditions. Causes include:
- Chronic kidney disease
- Polycystic kidney disease
- kidney tumor
- kidney failure
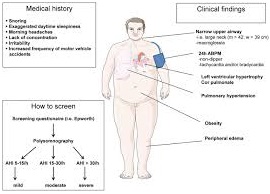
- Sleep apnea
- Tumors or other diseases of the adrenal gland
- Coarctation of the aorta
- Pregnancy
- preeclampsia
- Use of birth control pills
- Alcohol addiction
- Thyroid dysfunction
- Disorders of the adrenal gland
- Cushing’s syndrome
- Hyperaldosteronism
- pheochromocytoma
- Certain Drugs
- Corticosteroids
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- cold medications
Symptoms Of Secondary Hypertension:
The following symptoms may be exhibited by individuals suffering from secondary hypertension:
- Resistant hypertension- hypertension which doe not respond to medications
- Very high blood pressure
- Blood pressure medications which do not work anymore
- Sudden-onset high blood pressure before age 30 or after age 55
- No family history of high blood pressure
- No obesity
Diagnosis Of Secondary Hypertension:
Secondary hypertension, like pediatric and portal hypertension, is diagnosed via:
- Measuring the blood pressure
- Blood test
- Urinalysis, to identify the cause of the onset of the ailment
- Ultrasound of kidneys, since most of the causes of secondary hypertension are linked to medical conditions affected the kidney
Treatment Of Secondary Hypertension:
The following medications can be sued to combat secondary hypertension:
- Thiazide diuretics, to help the body eliminate sodium and water thereby reducing blood volume.
- Beta blocker, which reduce the workload on the heart and opens blood vessels. This in turn causes the heart to beat slower.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors which help relax blood vessels by blocking the formation of a natural chemical that narrows blood vessels.
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers which help relax blood vessels by blocking the action of a natural chemical that narrows blood vessels.
- Calcium channel blockers which help relax the muscles of the blood vessels
- Direct renin inhibitors.
By : Natural Health News