Tachycardia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What is Tachycardia?
Tachycardia is a common type of heart rhythm disorder (arrhythmia) in which the heart beats faster than normal while at rest.
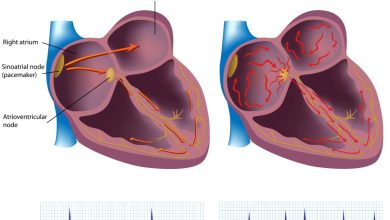
It’s normal for your heart rate to rise during exercise or as a physiological response to stress, trauma or illness (sinus tachycardia). But in tachycardia , the heart beats faster than normal in the upper or lower chambers of the heart or both while at rest. Your heart rate is controlled by electrical signals sent across heart tissues. Tachycardia occurs when an abnormality in the heart produces rapid electrical signals that quicken the heart rate, which is normally about 60 to 100 beats a minute at rest.
Causes of Tachycardia
The following situations, conditions and illnesses are possible causes:
- A reaction to certain medications
- Congenital (present at birth) electrical pathway abnormalities in the heart
- Congenital abnormalities of the heart
- Consuming too much alcohol
- Consumption of cocaine and some other recreational drugs
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Heart disease which has resulted in poor blood supply and damage to heart tissues, including coronary artery disease (atherosclerosis), heart valve disease, heart failure, heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy), tumors, or infections.
- Hypertension
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid gland)
- Smoking
- Certain lung diseases
Symptoms of Tachycardia
When your heart is beating too fast, it may not pump blood effectively to the rest of your body. This can deprive your organs and tissues of oxygen and can cause the following tachycardia-related symptoms:
- Shortness of breath
- Lightheadedness
- Rapid pulse rate
- Heart palpitations — a racing, uncomfortable or irregular heartbeat or a sensation of “flopping” in the chest
- Chest pain
- Fainting (syncope)
Diagnosis of Tachycardia
A thorough physical exam, medical history and testing is required to diagnose tachycardia.
Several heart tests also may be necessary to diagnose tachycardia.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Electrocardiogram
- Cardiac event monitor
- Holter monitor.
- Event monitor
- Electrophysiological test
- Cardiac imaging
- Echocardiogram
- Coronary angiogram
Types of cardiac imaging used to diagnose tachycardia include:
- Echocardiogram (echo).
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Computerized tomography (CT).
- Coronary angiogram.
- Chest X-ray. .
- Stress Test
- Tilt table test
Treatment of Tachycardia
There are several treatment options available for people who experience tachycardia. Tachycardia can be ventricular (in the lower chambers of the heart) or atrial (in the upper chambers of the heart). Your heart doctor will determine the treatment that’s best for your condition.
VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA TREATMENTS
- Medications
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)
VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION TREATMENTS
- External defibrillation
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)
- Medications
ATRIAL FLUTTER TREATMENTS
- Medications
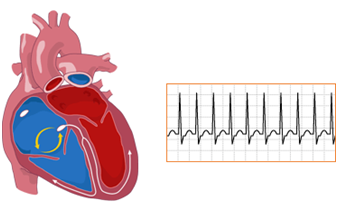
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION TREATMENTS
- Medications
- Cardiac catheter ablation
- Cardioversion
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)
- Surgery
By : Natural Health News