Testicular Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Testicular Cancer?
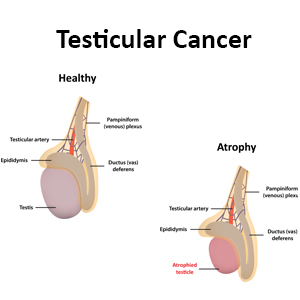
Testicular cancer is cancer that develops in the testicles, a part of the male reproductive system which is located inside the scrotum.
Testicular cancer, when compared to other types of cancer, is extremely are. However, it has the highest cure rate. It is highly treatable, regardless of the spread of the cancer.
The treatment depends upon the stage of cancer. If detected early, the cure rates are even higher.
It is the most common cancer in males aged 20–39 years, the period when it is most common to start, and is rarely seen before the age of 15 years.
Stages of testicular cancer include:
- Stage I: the cancer remains localized to the testis.
- Stage II: the cancer involves the testis and metastasis to retroperitoneal and/or paraaortic lymph nodes (lymph nodes below the diaphragm).
- Stage III: the cancer involves the testis and metastasis beyond the retroperitoneal and paraaortic lymph nodes. Stage 3 is further subdivided into non-bulky stage 3 and bulky stage 3
Causes Of Testicular Cancer:
The causes of testicular cancer is not known, but a number of factors have been identified that increase the chance of developing the condition.
These include:
- having a family history of testicular cancer
- Being born with undescended testicles (cryptorchidism).
- Abnormal testicle development
- Being between the ages of 15 and 35
- Being a white male
Symptoms Of Testicular Cancer:
Testicular cancer may exhibit the following symptoms:
- a lump in one testis which may or may not be painful
- sharp pain or a dull ache in the lower abdomen or scrotum
- a feeling often described as “heaviness” in the scrotum
- breast enlargement (gynecomastia) from hormonal effects of β-hCG
- low back pain (lumbago) due to the cancer spreading to the lymph nodes along the back
Diagnosis Of Testicular Cancer:
Testicular cancer may be diagnosed via:
- A testicular self-examination conducted by the affected individual
- Physical examination, to detect presence of lumps
- Ultrasound, which help determine the nature of any testicular lumps, such as if the lumps are solid or fluid-filled. It also helps in telling whether lumps are inside or outside of the testicle.
- Blood tests, to determine the levels of tumor markers in your blood.
- Surgery to remove a testicle (radical inguinal orchiectomy), to determine whether the tumor is malignant or benign.
- CT scan, in order to determine the stage of the testicular cancer
Treatment Of Testicular Cancer:
The following treatment options are available:
- Surgery
Surgery to remove entire testicle
Surgery to remove nearby lymph nodes - Radiation
- Chemotherapy
Related Articles:
Esophageal Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Thyroid Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Vaginal Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Rectal Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Vulvar Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Gallbladder Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Pancreatic Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Case Seeking Cancer Screenings Heads To Trial
Solid Organ Transplant Patients At Higher Cancer Death Risk
A Sort Of Prostate Cancer Treatment May Upsurge Probabilities Of Alzheimer’s
Oral Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Ovarian Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Alkaline Diet Helping In Cancer and Other Syndromes
By : Natural Health News