Tetralogy Of Fallot Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Tetralogy Of Fallot ?
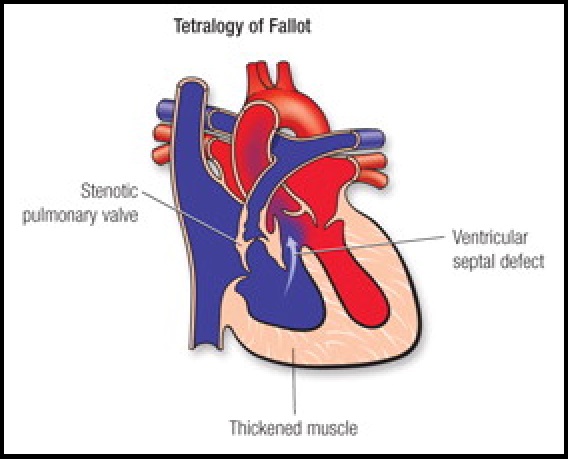
Tetralogy of fallot is a congenital heart defect. It is an umbrella term for four anatomical abnormalities which include:
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
- Overriding aorta − enlargement of aortic valve which appears to arise from both the left and right ventricles instead of the left ventricle as in normal hearts
- Pulmonary stenosis− narrowing of the pulmonary valve and outflow tract
- Right ventricular hypertrophy− thickening of the muscular walls of the right ventricle, which occurs when the right ventricle is pumping blood at high pressure
These defects cause oxygen-poor blood to flow out of the heart and to the rest of the body. Thereby, tetralogy of fallot is the most common cause of blue baby syndrome and is one of the most common cyanotic heart defects.
Along with tetralogy of fallot, those affected may also develop additional ventricular septal defects. . Some patients with tetralogy of Fallot have complete obstruction to flow from the right ventricle.
Causes Of Tetralogy Of Fallot:
The exact cause of tetralogy of fallot is yet unknown. However, it is thought to arise from a combination of environmental and genetic factors.
Specific genetic associations include:
- JAG1
- NKX2-5
- ZFPM2
- VEGF
Some conditions or factors that occur during pregnancy may increase the risk of having a child who has tetralogy of Fallot. These may include:
- German measles (rubella) and some other viral illnesses
- Poor nutrition
- Alcohol use
- Age (being older than 40)
- Diabetes
- Presence of down syndrome or Digeorge syndrome
Symptoms Of Tetralogy Of Fallot:
The following signs and symptoms are exhibited by babies suffering from tetralogy of fallot:
- A “tet spell” characterized by bluish coloration of the skin caused by blood low in oxygen (cyanosis)
- Shortness of breath and rapid breathing, especially during feeding or exercise
- Loss of consciousness
- Clubbing of fingers and toes
- Poor weight gain
- Tiring easily during play or exercise
- Irritability
- Prolonged crying
- A heart murmur
- Not respond to a parent’s voice or touch
- Becoming very fussy
Diagnosis Of Tetralogy Of Fallot:
Tetralogy of fallot can be diagnosed via:
- Failure to respond to “hyperoxia test”
- Detection of a loud murmur during examination
- Echocardiography
- Electrocardiogram
- Chest x-ray
- Cardiac catheterization
Treatment Of Tetralogy Of Fallot:
The only treatment option available for tetralogy of fallot is surgery.
The type of surgery may depend on the condition of the individual. The following surgical options are available:
- Intracardiac repair
- Palliatative surgery
By : Natural Health News




