Thrombophlebitis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
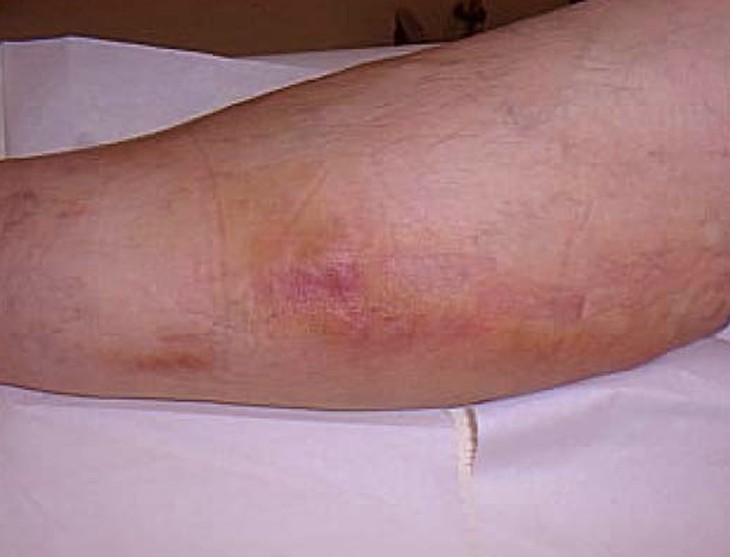
What is Thrombophlebitis?
Thrombophlebitis is inflammation of a vein that’s caused by a blood clot. It typically occurs in the legs. A blood clot is a solid formation of blood cells that clump together. Blood clots can interfere with the normal flow of blood throughout your body. Therefore, they’re considered dangerous. Thrombophlebitis can occur in veins near the surface of your skin or deeper down in between your muscle layers.
Causes of Thrombophlebitis
The causes of Thrombophlebitis are:
- Varicose veins – many cases occur in people who have varicose veins of the legs. Varicose veins are prone to minor injuries which can lead to inflammation.
- Intravenous injection or cannulation – sometimes it occurs after having injections into the veins (intravenous injections) or ‘drips’ (intravenous infusions) in hospital. These are commonly given in hand or arm veins. Such procedures can injure the vein and may trigger inflammation. Damage to the veins in this way is also common in people who inject ‘street drugs’.
- Previous problems with veins – if someone has had previous superficial thrombophlebitis or a previous DVT, they are more likely to get superficial thrombophlebitis.
- Abnormalities of blood clotting factors – various conditions can alter certain chemicals (clotting factors) in the bloodstream, which make the blood clot more easily. These include using the oral contraceptive pill, using hormone replacement therapy, cancer, smoking and pregnancy. There are also some less common hereditary blood disorders where blood clots develop more readily than usual.
- Blood flowing more slowly than normal (stasis) – this might occur in veins that are varicose, during long flights or in people who are immobile, and also following major surgery.
Symptoms of Thrombophlebitis
Symptoms of Thrombophlebitis include:
- Redness and inflammation of the skin along a vein
- Warmth of the skin and tissue around the vein
- Tenderness and pain that worsens with added pressure
- Pain in the limb
- Darkening of the skin over the vein
- Hardening of the vein
Diagnosis of Thrombophlebitis
The health care provider can usually diagnose the condition based on how the affected area looks. Your provider will frequently check your vital signs. This is to make sure you don’t have complications.
If the cause cannot be easily identified, 1 or more of the following tests may be done:
- Blood coagulation studies
- Doppler ultrasound
- Venography
Treatment of Thrombophlebitis
Support stockings and wraps can help to reduce discomfort. Your provider may prescribe medicines such as:
- Painkillers
- Blood thinners to prevent new clots from forming, most often only prescribed when deep veins are involved
- Medicines such as ibuprofen to reduce pain and swelling
- Medicines injected into the vein to dissolve an existing clot
You may be told to do the following:
- Keep pressure off the area to reduce pain and decrease the risk of further damage.
- Raise the affected area to reduce swelling.
Rare treatment options are:
- Surgical removal of a vein near the surface
- Vein stripping
- Bypass of the vein
Related Articles:
Melasma Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Oedema Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Tinea Pedis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Tinea Faciei Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Thrombocytopenia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Torticollis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Eczema Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Toxic Shock Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Tarsal Cyst Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
By : Natural Health News




