Tinea Pedis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
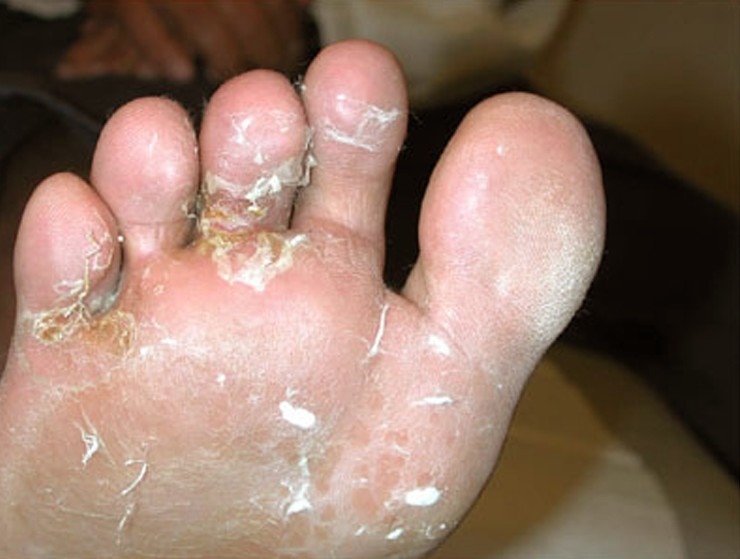
What is Tinea Pedis?
Athlete’s foot also called Tinea Pedis is a contagious fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet and can spread to the toenails and sometimes the hands. The fungal infection is called athlete’s foot because it’s commonly seen in athletes.
Causes of Tinea Pedis
Tinea Pedis is a fungal infection of the foot caused by parasites on the skin called dermatophytes. They are called parasites as they live off other organisms in order to survive.
Dermatophytes can be divided into three groups according to their favorite hosts:
- Fungi preferring soil (geophile)
- Fungi preferring animals (zoophile)
- Fungi preferring humans (anthropophile).
Tinea Pedis is usually caused by anthropophile fungi. The most common species are Microsporum, Epidermophyton and Trichophyton. These account for 90 per cent of all skin fungal infections, commonly referred to as ringworm (tinea corporis).
The medical terms for athlete’s foot are tinea pedis or dermatophytosis palmaris, plantaris and interdigitalis – the latter indicates that, in addition to the soles and toes of the feet, the palms of the hands can also become infected.
Symptoms of Tinea Pedis
There are many possible symptoms of Tinea Pedis. You may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
•Itching, stinging, and burning between the toes
•Itching, stinging, and burning on the soles of the feet
•Blisters on the feet that itch
•Cracking and peeling skin on the feet, most commonly between the toes and on the soles
•Dry skin on the soles or sides of the feet
•Raw skin on the feet
•Discolored, thick, and crumbly toenails
•Toenails that pull away from the nail bed
Diagnosis of Tinea Pedis
Diagnosis is confirmed by skin scraping which is then viewed under a microscope in potassium hydroxide, followed by culture.
Generally a clinical diagnosis is sufficient to warrant starting treatment, providing it is recognised that there are other causes of interdigital infection.
Treatment of Tinea Pedis
Tinea Pediscan often be treated with over-the-counter (OTC) topical antifungal medications. If OTC medications don’t successfully treat the fungal infection, your doctor may prescribe topical or oral prescription-strength antifungal medications. Your doctor may also recommend home treatments to help clear up the infection.
OTC Medications
There are many OTC topical antifungal medications, including:
•Miconazole (Desenex)
•Terbinafine (Lamisil AT)
•Clotrimazole (Lotrimin AF)
•Butenafine (Lotrimin Ultra)
Related Articles:
Melasma Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Oedema Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Tinea Faciei Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Thrombophlebitis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Thrombocytopenia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Torticollis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Eczema Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Toxic Shock Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Tarsal Cyst Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
By : Natural Health News




