Type 1 Diabetes Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
What Is Type 1 Diabetes ?
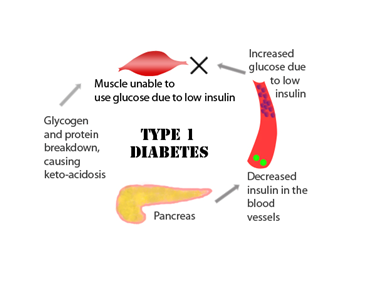
Type 1 diabetes, once known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin, a hormone needed to allow sugar (glucose) to enter cells to produce energy. The far more common type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t make enough insulin.
Various factors may contribute to type 1 diabetes, including genetics and exposure to certain viruses. Although type 1 diabetes usually appears during childhood or adolescence, it also can begin in adults.
Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes
The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is not yet known, but we do know it has a strong family link and cannot be prevented. We also know that it has nothing to do with lifestyle, although maintaining a healthy lifestyle is very important in helping to manage type 1 diabetes.
At this stage nothing can be done to prevent or cure type 1 diabetes.
Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes happens most often in children and young adults but can appear at any age. Symptoms may include
- Being very thirsty
- Urinating often
- Feeling very hungry or tired
- Losing weight without trying
- Having sores that heal slowly
- Having dry, itchy skin
- Losing the feeling in your feet or having tingling in your feet
- Having blurry eyesight
Diagnosis Of Type 1 Diabetes
Diagnoses of Type 1 Diabetes are as follows:
- Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test
- Random blood sugar test.
- Fasting blood sugar test
Further blood tests, to check for autoantibodies that are common in type 1 diabetes. These tests help to distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The presence of ketones byproducts from the breakdown of fat in your urine also suggests type 1 diabetes, rather than type 2.
Treatment Of Type 1 Diabetes
Treatment for type 1 diabetes includes:
- Taking insulin
- Carbohydrate counting
- Frequent blood sugar monitoring
- Eating healthy foods
- Exercising regularly and maintaining a healthy weight
Insulin and other medications
Types of insulin are many and include:
- Rapid-acting insulin
- Long-acting insulin
- Intermediate options
Examples are regular insulin (Humulin 70/30, Novolin 70/30, others), insulin isophane (Humulin N, Novolin N), insulin glulisine (Apidra), insulin lispro (Humalog) and insulin aspart (Novolog). Long-acting insulins include glargine (Lantus) and detemir (Levemir).
Insulin administration
- Injections.
- An insulin pump
Artificial pancreas
Additional medications also may be prescribed for people with type 1 diabetes, such as:
- Pramlintide (Symlin).
- High blood pressure medications.
- Aspirin.
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Related Articles:
Papaya is Good for Diabetics and Other Health Benefits
Diabetes Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Diabetes Insipidus Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Gestational Diabetes Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Type 2 Diabetes Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
The Blood Sugar Diet That Will Make a Difference in Blood Sugar Levels
Fruits as Natural Remedies for Diabetes
7 Best Natural Herbs for Diabetes and its Healthy Benefits
Diabetes – A Healthy Diet Plan
Diabetes Friendly 1600 Calorie Diabetic Diet Plan
The Diabetes Diet and Food Supplements
Diabetes Diet Plan for Kids – Weight Loss Diet Plans
By : Natural Health News




