Type 2 Diabetes Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
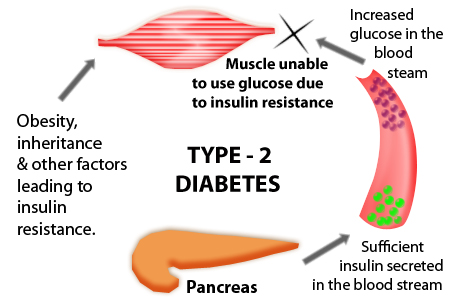
Type 2 diabetes is a long term metabolic disorder. It affects the way glucose is metabolized by the body. In most cases, it is characterized by resistance of the body against effects of insulin.
It is marked by high blood pressure and relative lack of insulin, in contrast to absolute lack of insulin in type 1 diabetes.
It primarily occurs due to obesity and lack of exercise in those who are genetically predisposed. Most cases of diabetes are type 2 in nature.
Various complications may stem from Type 2 diabetes. These may include:
- Heart disease
- Strokes
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Blindness
- Kidney failure
- Amputation of feet
Type 2 diabetes can be prevented in some cases by staying within the normal weight as measured by BMI.
Over the years, number of people diagnosed with type 2 diabetes has increased steadily. It generally begins in older age and therefore is also referred to as adult onset diabetes. There is no known cure against type 2 diabetes, although it can be effectively managed.
Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes:
The development of type 2 diabetes is caused by a combination of lifestyle and genetic factors. Such factors encompass:
- Lifestyle
Obesity
Lack of physical exercise
Stress
Poor diet
Urbanization
Persistent organic pollutants - Genetic
Difference in DNA that affects how the body makes insulin - Medical conditions
Acromegaly
Cushing’s syndrome
hyperthyroidism
pheochromocytoma
Glucagonomas.
Testosterone deficiency
Metabolic syndrome
Possible Risk Factors Include:
- Fat distribution marked by fat stored primarily in the abdomen
- Family history
- Being middle or old aged
- Having prediabetes
- Having polycystic ovarian syndrome
Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes:
The following symptoms may be exhibited:
- Frequent urination (polyuria)
- Increased thirst (polydipsia)
- Increased hunger (Polyphagia)
- Weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Itchiness
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Recurrent vaginal infections
- Developing sores that do not heal
- fatigue
Diagnosis Of Type 2 Diabetes:
The following tests help confirm the diagnosis:
- Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test, which indicates average blood sugar level for the past two to three months.
- Random blood sugar test.
- Fasting blood sugar test.
- Oral glucose tolerance test.
Treatment Of Type 2 Diabetes:
Type 2 diabetes can be treated in the following ways:
- Eating healthy
- Exercising
- Monitoring blood sugar
- Medications and insulin therapy
Metformin (Glucophage, Glumetza, others).
Sulfonylureas.
Meglitinides.
Thiazolidinediones.
DPP-4 inhibitors.
GLP-1 receptor agonists.
SGLT2 inhibitors
Related Articles:
Papaya is Good for Diabetics and Other Health Benefits
Diabetes Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Diabetes Insipidus Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Gestational Diabetes Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
The Blood Sugar Diet That Will Make a Difference in Blood Sugar Levels
Fruits as Natural Remedies for Diabetes
7 Best Natural Herbs for Diabetes and its Healthy Benefits
Diabetes – A Healthy Diet Plan
Diabetes Friendly 1600 Calorie Diabetic Diet Plan
The Diabetes Diet and Food Supplements
Diabetes Diet Plan for Kids – Weight Loss Diet Plans
Type 1 Diabetes Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
By : Natural Health News




