Vascular Dementia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What is Vascular Dementia?
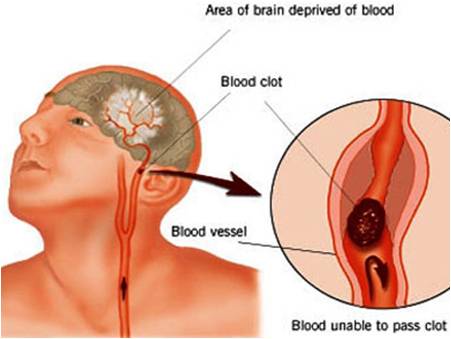
Vascular Dementia is a general term describing problems with reasoning, planning, judgment, memory and other thought processes caused by brain damage from impaired blood flow to the brain.
It is caused by problems in the supply of blood to the brain, typically a series of minor strokes, leading to step wise cognitive decline.
Vascular syndrome refers to a syndrome consisting of a complex interaction of cerebrovascular disease and risk factors that lead to changes in the brain structures due to strokes and lesions, and resulting changes in cognition.
The temporal relationship between a stroke and cognitive deficits is needed to make the diagnosis.
Causes of Vascular Dementia:
Vascular dementia may be causes due to one of the following reasons:
- Stroke (infarction) blocking a brain artery.
Strokes that block a brain artery usually cause a range of symptoms that may include vascular dementia.
- Narrowed or chronically damaged brain blood vessels.
Conditions that narrow or inflict long-term damage on the brain blood vessels also can lead to vascular dementia. These conditions include:
- The wear and tear associated with aging
- High blood pressure
- Hardening of the arteries
- Diabetes
- Lupus erythematosus
- Brain hemorrhage
- Temporal arteritis.
- Cerebral amyloid angiopathy, which involves accumulation of betaamyloid plaques in the walls of the cerebral arteries, leading to breakdown and rupture of the vessels.
The following factors increase the Risk of developing Vascular Dementia:
- Increasing age
- History of Heart Attack, strokes or mini strokes
- Atherosclerosis
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Atrial fibrillation
Symptoms of Vascular Dementia:
The following symptoms are exhibited:
- Confusion
- Disorientation
- Trouble speaking or understanding speech
- Vision loss
- Trouble paying attention and concentrating
- Reduced ability to organize thoughts or actions
- Decline in ability to analyze a situation, develop an effective plan and communicate that plan to others
- Difficulty deciding what to do next
- Problems with memory
- Restlessness and agitation
- Unsteady gait
- Sudden or frequent urge to urinate or inability to control passing urine
- Depression
Diagnosis of Vascular Dementia:
The following tests and exams are conducted in order to diagnose vascular dementia:
- Lab test
- Blood pressure
- Cholesterol
- Blood sugar
- Neurological exam
- Brain imaging
- CT scans
- MRI
- Carotid ultrasound
- Neuropsychological tests
Treatment of Vascular Dementia:
Vascular dementia can be treated in the following ways:
- Controlling underlying conditions and risk factors
- Lowering blood pressure
- Reducing cholesterol level
- Preventing blood from clotting and keep your arteries clear
- Help control blood sugar if have diabetes
- Intake of Alzheimer’s medication
- Cholinesterase inhibitors
(a)donepezil (Aricept)
(b)galantamine (Razadyne)
(c)rivastigmine (Exelon)
2. Memantine
By : Natural Health News




