Vulvodynia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Vulvodynia?
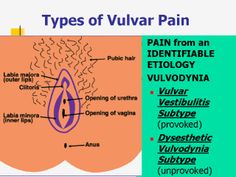
Vulvodynia is a chronic pain syndrome that affects the vulvar area and occurs without an identifiable cause.
Vulvodynia can be divided into two subtypes:
- Generalized Vulvodynia
It is accompanied by pain in different areas of the vulva at different time periods. Vulvar pain may be constant or random.
- Vulvar vestibulitis syndrome
Marked by pain in the vestibule, which is the entrance to the vagina, this type of vulvar pain comes on only after touch or pressure, such as during intercourse.
Causes Of Vulvodynia:
To this date, doctors don’t know the exact cause for Vulvodynia.
Researchers have come up with possible explanations which include:
- Nerve injury or irritation
- Abnormal response in vulvar cells to an infection or trauma
- Genetic factors that make the vulva respond poorly to chronic inflammation
- Hypersensitivity to yeast infections
- Muscle spasms
- Allergies or irritation to chemicals or other substances
- Hormonal changes
- History of sexual abuse
- Frequent antibiotic use
Symptoms Of Vulvodynia:
Symptoms of Vulvodynia are known to start suddenly and persist for years.
The major symptom is pain in the genital area which can be characterized by:
- Burning
- Soreness
- Stinging
- Rawness
- Painful intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Throbbing
- Itching
One may feel the symptoms arise:
- all the time or just once in a while
- during activities such as exercise, intercourse, or walking — or even while at rest
- while bicycling, inserting tampons, or even sitting
- in one specific area or throughout your entire vulva
Diagnosis Of Vulvodynia:
The following tests and exam are likely to be done in order to diagnose Vulvodynia:
- Pelvic exam
- Cotton swab test
- Wet mount
- Vaginal pH
- Fungal culture,
- Gram stain
Treatment Of Vulvodynia:
Although it is incurable, self-care and treatments for Vulvodynia can help bring relief from symptoms.
Treatment may include:
Steroids, tricyclic antidepressants or anticonvulsants may help lessen chronic pain. Moreover, Antihistamines may be used to reduce itching.
- Biofeedback therapy.
This therapy can help reduce pain by teaching how to control how the body responds to the symptoms. To cope with Vulvodynia, biofeedback can teach one to relax the pelvic muscles, which can contract in anticipation of pain and actually cause chronic pain.
- Local anesthetics.
Medications, such as lidocaine ointment, can provide temporary symptom relief.
- Nerve blocks.
Women who have long-standing pain that doesn’t respond to other treatments may benefit from local injections of nerve blocks.
- Pelvic floor therapy.
Exercises to relax muscles of the pelvic floor may help relieve vulvodynia pain.
In cases of localized vulvodynia or vestibulodynia, surgery to remove the affected skin and tissue (vestibulectomy) relieves pain in some women.
By : Natural Health News




